Page 86 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 86
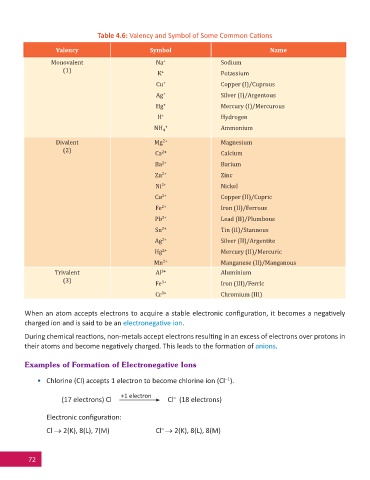
Table 4.6: Valency and Symbol of Some Common Ca ons
Valency Symbol Name
Monovalent Na + Sodium
(1) K + Potassium
Cu + Copper (I)/Cuprous
Ag + Silver (I)/Argentous
Hg + Mercury (I)/Mercurous
H + Hydrogen
NH 4 + Ammonium
Divalent Mg 2+ Magnesium
(2) Ca 2+ Calcium
Ba 2+ Barium
Zn 2+ Zinc
Ni 2+ Nickel
Cu 2+ Copper (II)/Cupric
Fe 2+ Iron (II)/Ferrous
Pb 2+ Lead (II)/Plumbous
Sn 2+ Tin (II)/Stannous
Ag 2+ Silver (II)/Argentite
Hg 2+ Mercury (II)/Mercuric
Mn 2+ Manganese (II)/Manganous
Trivalent Al 3+ Aluminium
(3) Fe 3+ Iron (III)/Ferric
Cr 3+ Chromium (III)
When an atom accepts electrons to acquire a stable electronic confi gura on, it becomes a nega vely
charged ion and is said to be an electronega ve ion.
During chemical reac ons, non-metals accept electrons resul ng in an excess of electrons over protons in
their atoms and become nega vely charged. This leads to the forma on of anions.
Examples of Formation of Electronegative Ions
–1
• Chlorine (Cl) accepts 1 electron to become chlorine ion (Cl ).
+1 electron
–
(17 electrons) Cl Cl (18 electrons)
Electronic confi gura on:
–
Cl 2(K), 8(L), 7(M) Cl 2(K), 8(L), 8(M)
72