Page 81 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 81
Activity 4.1
Aim: To fi nd out and write the isotopes of given elements.
Find out and write isotopes of oxygen, sulphur and chlorine.
Properties of Isotopes
• The isotopes of an element have same atomic number. Thus, the number of electrons are also
same.
• The isotopes of an element show same chemical proper es because they have same atomic
number.
• Mass-dependent proper es such as density, mel ng point and boiling point diff er in diff erent
isotopes. This is because the mass of isotopes diff ers slightly.
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
Electrons are arranged in diff erent shells around the nucleus of the atom of an element. The arrangement
of electrons in diff erent orbits or shells around the nucleus of an atom is called its electronic confi gura on.
We can write down the electronic confi gura on of an element if we know:
• The number of electrons present in an atom of the element and
• The maximum number of electrons which can be accommodated in diff erent energy shells of the
atom.
• Each orbit or shell has a fi xed or defi nite amount of energy.
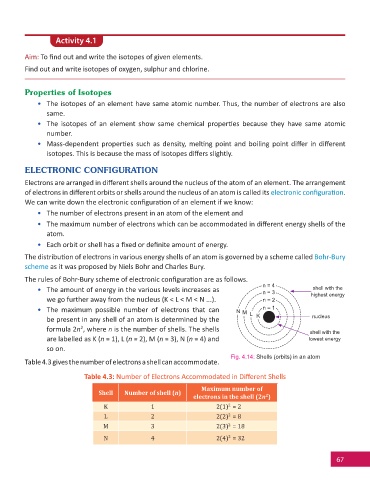
The distribu on of electrons in various energy shells of an atom is governed by a scheme called Bohr-Bury
scheme as it was proposed by Niels Bohr and Charles Bury.
The rules of Bohr-Bury scheme of electronic confi gura on are as follows.
n = 4
shell with the
• The amount of energy in the various levels increases as n = 3 highest energy
we go further away from the nucleus (K < L < M < N ...). n = 2
• The maximum possible number of electrons that can N M L n = 1
be present in any shell of an atom is determined by the K nucleus
2
formula 2n , where n is the number of shells. The shells shell with the
are labelled as K (n = 1), L (n = 2), M (n = 3), N (n = 4) and lowest energy
so on.
Fig. 4.14: Shells (orbits) in an atom
Table 4.3 gives the number of electrons a shell can accommodate.
Table 4.3: Number of Electrons Accommodated in Diff erent Shells
Maximum number of
Shell Number of shell (n)
2
electrons in the shell (2n )
K 1 2(1) = 2
2
2
L 2 2(2) = 8
2
M 3 2(3) = 18
N 4 2(4) = 32
2
67