Page 76 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 76
Bohr’s Atomic Model
In 1913, Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist, proposed a modifi ed version of Rutherford’s atomic model. The
main features of his model are as follows.
• Electrons revolve around the nucleus in fi xed circular orbiter shells. They move the same way as
planets revolve around the sun.
• These shells have a fi xed size and energy. The shell nearest to the nucleus has the minimum energy
and as we go farther the energy increases.
Bohr labelled the shells as K,L,M,N,..., star ng from the innermost shell.
Discovery of Neutron
By the me Rutherford gave his model of the atom,
Know Your Scientist
it was found that the mass of an atom was en rely
concentrated within the nucleus in the form of protons, Ernest Rutherford (1871–1937) was a
since electrons had negligible mass. However, during New Zealand born Bri sh physicist. He is
subsequent experiments, it was found that the mass known for his 1899 discovery which stated
of an atom is far more than the total mass of protons that there were at least two dis nct types
present in the atom. It was realised that another of radia on—alpha radia on and beta
radia on.
subatomic par cle should be present in the nucleus
that had mass but no electric charge. Neutron was
discovered in 1932 by James Chadwick.
Properties of Neutrons Thirst for Knowledge
• Neutron is an integral part of an atom and is • The protons and neutrons present in
present inside the nucleus. the nucleus of an atom are collec vely
called nucleons.
• It is of the same size as that of a proton.
1
• A neutron is represented by n . The
0
• It is electrically neutral, i.e., it has no charge. superscript 1 represents 1 which is its
mass and the subscript 0 represents
zero charge.
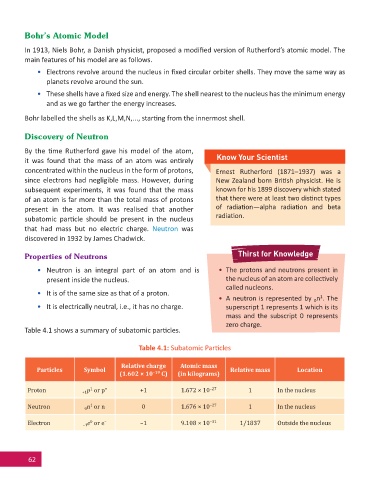
Table 4.1 shows a summary of subatomic par cles.
Table 4.1: Subatomic Par cles
Relative charge Atomic mass
Particles Symbol Relative mass Location
(1.602 × 10 –19 C) (in kilograms)
Proton +1 p or p + +1 1.672 × 10 –27 1 In the nucleus
1
1
Neutron 0 n or n 0 1.676 × 10 –27 1 In the nucleus
0
Electron –1 e or e – –1 9.108 × 10 –31 1/1837 Outside the nucleus
62