Page 72 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 72
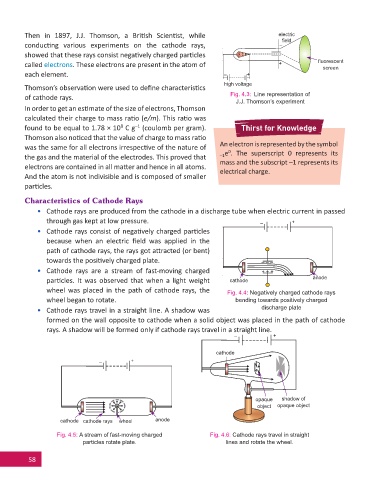
Then in 1897, J.J. Thomson, a Bri sh Scien st, while electric
fi eld
conduc ng various experiments on the cathode rays, –
showed that these rays consist nega vely charged par cles
called electrons. These electrons are present in the atom of + fl uorescent
screen
each element. – +
high voltage
Thomson’s observa on were used to defi ne characteris cs
Fig. 4.3: Line representation of
of cathode rays.
J.J. Thomson’s experiment
In order to get an es mate of the size of electrons, Thomson
calculated their charge to mass ra o (e/m). This ra o was
8
–1
found to be equal to 1.78 × 10 C g (coulomb per gram). Thirst for Knowledge
Thomson also no ced that the value of charge to mass ra o
An electron is represented by the symbol
was the same for all electrons irrespec ve of the nature of
0
e . The superscript 0 represents its
the gas and the material of the electrodes. This proved that –1
mass and the subscript –1 represents its
electrons are contained in all ma er and hence in all atoms.
electrical charge.
And the atom is not indivisible and is composed of smaller
par cles.
Characteristics of Cathode Rays
• Cathode rays are produced from the cathode in a discharge tube when electric current in passed
through gas kept at low pressure. – +
• Cathode rays consist of nega vely charged par cles
because when an electric fi eld was applied in the
path of cathode rays, the rays got a racted (or bent)
towards the posi vely charged plate. – – –
• Cathode rays are a stream of fast-moving charged + + +
anode
par cles. It was observed that when a light weight cathode
wheel was placed in the path of cathode rays, the Fig. 4.4: Negatively charged cathode rays
wheel began to rotate. bending towards positively charged
discharge plate
• Cathode rays travel in a straight line. A shadow was
formed on the wall opposite to cathode when a solid object was placed in the path of cathode
rays. A shadow will be formed only if cathode rays travel in a straight line.
– +
cathode
– +
opaque shadow of
object opaque object
cathode cathode rays wheel anode
Fig. 4.5: A stream of fast-moving charged Fig. 4.6: Cathode rays travel in straight
particles rotate plate. lines and rotate the wheel.
58