Page 89 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 89
Sulphite (SO ) 2– 2
3
Carbonate (CO ) 2– 2
3
Dichromate (Cr O ) 2– 2
7
2
Phosphate (PO ) 3– 3
4
CHEMICAL BOND
Atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to achieve stability. The bond formed between
two atoms when they combine is called a chemical bond. A chemical bond is the force of a rac on
which holds two or more atoms together in a molecules. Atoms can combine either by transferring or
by sharing electrons.
Electrovalent Bond
The chemical bond formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to the other is
called an electrovalent or ionic bond and the compounds so formed are called electrovalent or ionic
compounds. An electrovalent bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
Ca ons are the par cles having posi ve charge and anions are the par cles having nega ve charge.
The opposite charges get a racted to each other due to the presence of strong electrosta c force of
a rac on. The forma on of the bond takes place between an anion and a ca on, and hence is also
called ionic bond.
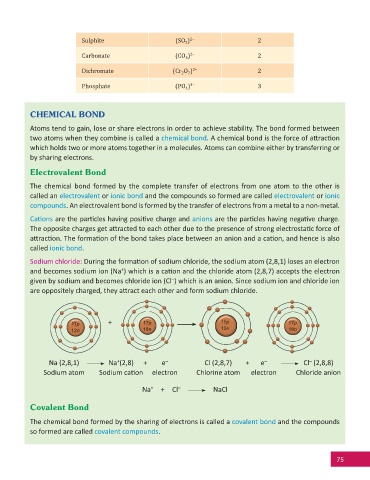
Sodium chloride: During the forma on of sodium chloride, the sodium atom (2,8,1) loses an electron
+
and becomes sodium ion (Na ) which is a ca on and the chloride atom (2,8,7) accepts the electron
–
given by sodium and becomes chloride ion (Cl ) which is an anion. Since sodium ion and chloride ion
are oppositely charged, they a ract each other and form sodium chloride.
11p + 17p 11p 17p
12n 18n 12n 18n
–
+
Na (2,8,1) Na (2,8) + e – Cl (2,8,7) + e – Cl (2,8,8)
Sodium atom Sodium ca on electron Chlorine atom electron Chloride anion
+
Na + Cl – NaCl
Covalent Bond
The chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons is called a covalent bond and the compounds
so formed are called covalent compounds.
75