Page 329 - Start Up Mathematics_8 (Non CCE)
P. 329
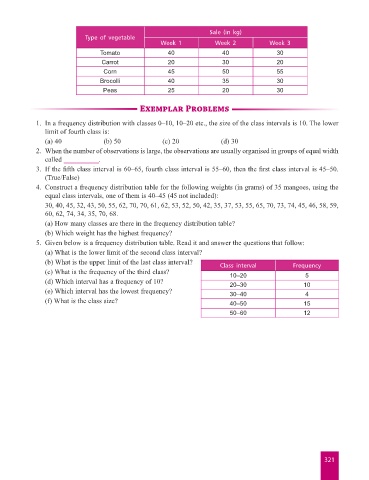
Sale (in kg)
Type of vegetable
Week 1 Week 2 Week 3
Tomato 40 40 30
Carrot 20 30 20
Corn 45 50 55
Brocolli 40 35 30
Peas 25 20 30
Exemplar Problems
1. In a frequency distribution with classes 0–10, 10–20 etc., the size of the class intervals is 10. The lower
limit of fourth class is:
(a) 40 (b) 50 (c) 20 (d) 30
2. When the number of observations is large, the observations are usually organised in groups of equal width
called __________.
3. If the fifth class interval is 60–65, fourth class interval is 55–60, then the first class interval is 45–50.
(True/False)
4. Construct a frequency distribution table for the following weights (in grams) of 35 mangoes, using the
equal class intervals, one of them is 40–45 (45 not included):
30, 40, 45, 32, 43, 50, 55, 62, 70, 70, 61, 62, 53, 52, 50, 42, 35, 37, 53, 55, 65, 70, 73, 74, 45, 46, 58, 59,
60, 62, 74, 34, 35, 70, 68.
(a) How many classes are there in the frequency distribution table?
(b) Which weight has the highest frequency?
5. Given below is a frequency distribution table. Read it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) What is the lower limit of the second class interval?
(b) What is the upper limit of the last class interval? Class interval Frequency
(c) What is the frequency of the third class? 10–20 5
(d) Which interval has a frequency of 10? 20–30 10
(e) Which interval has the lowest frequency? 30–40 4
(f) What is the class size? 40–50 15
50–60 12
321