Page 55 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 55
Crystallisation
The process of separa ng a solid dissolved in a liquid to make a solu on is called crystallisa on. This is
done by warming the solu on and allowing the solvent to evaporate thus leaving a saturated solu on.
We can obtain pure sugar from its solu on in water
by crystallisa on. This is done by hea ng the sugar Know Your Scientist
solu on in such a way that the water evaporates. Robert Boyle (1627–1691): Being the fi rst
When very li le amount of water is le , the solu on modern chemist, Boyle was one of the earliest
is cooled. The dissolved sugar separates in the form of men to apply scien fi c methods in chemistry
crystals on cooling. Crystals are solid par cles having and physics.
defi nite shape and size. The sugar crystals obtained
are cubical and shiny in appearance.
Froth Floatation
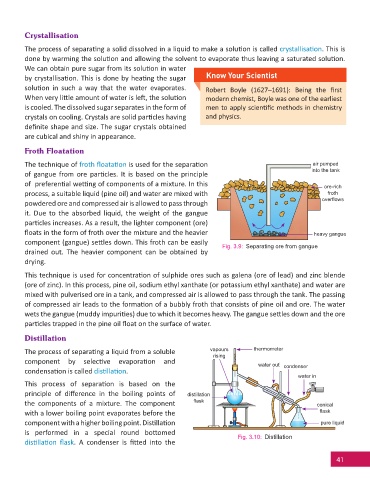
The technique of froth fl oata on is used for the separa on air pumped
into the tank
of gangue from ore par cles. It is based on the principle
of preferen al we ng of components of a mixture. In this ore-rich
process, a suitable liquid (pine oil) and water are mixed with froth
overfl ows
powdered ore and compressed air is allowed to pass through
it. Due to the absorbed liquid, the weight of the gangue
par cles increases. As a result, the lighter component (ore)
fl oats in the form of froth over the mixture and the heavier heavy gangue
component (gangue) se les down. This froth can be easily
Fig. 3.9: Separating ore from gangue
drained out. The heavier component can be obtained by
drying.
This technique is used for concentra on of sulphide ores such as galena (ore of lead) and zinc blende
(ore of zinc). In this process, pine oil, sodium ethyl xanthate (or potassium ethyl xanthate) and water are
mixed with pulverised ore in a tank, and compressed air is allowed to pass through the tank. The passing
of compressed air leads to the forma on of a bubbly froth that consists of pine oil and ore. The water
wets the gangue (muddy impuri es) due to which it becomes heavy. The gangue se les down and the ore
par cles trapped in the pine oil fl oat on the surface of water.
Distillation
The process of separa ng a liquid from a soluble vapours thermometer
rising
component by selec ve evapora on and
water out condenser
condensa on is called dis lla on.
water in
This process of separa on is based on the
principle of diff erence in the boiling points of distillation
the components of a mixture. The component fl ask conical
with a lower boiling point evaporates before the fl ask
component with a higher boiling point. Dis lla on pure liquid
is performed in a special round bo omed
Fig. 3.10: Distillation
dis lla on fl ask. A condenser is fi ed into the
41