Page 59 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 59
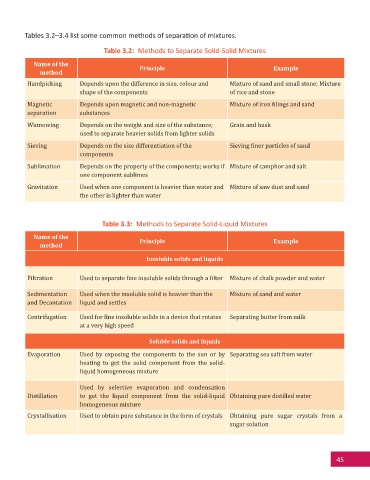
Tables 3.2–3.4 list some common methods of separa on of mixtures.
Table 3.2: Methods to Separate Solid-Solid Mixtures
Name of the Principle Example
method
Handpicking Depends upon the difference in size, colour and Mixture of sand and small stone; Mixture
shape of the components of rice and stone
Magnetic Depends upon magnetic and non-magnetic Mixture of iron ilings and sand
separation substances
Winnowing Depends on the weight and size of the substance; Grain and husk
used to separate heavier solids from lighter solids
Sieving Depends on the size differentiation of the Sieving iner particles of sand
components
Sublimation Depends on the property of the components; works if Mixture of camphor and salt
one component sublimes
Gravitation Used when one component is heavier than water and Mixture of saw dust and sand
the other is lighter than water
Table 3.3: Methods to Separate Solid-Liquid Mixtures
Name of the Principle Example
method
Insoluble solids and liquids
Filtration Used to separate ine insoluble solids through a ilter Mixture of chalk powder and water
Sedimentation Used when the insoluble solid is heavier than the Mixture of sand and water
and Decantation liquid and settles
Centrifugation Used for ine insoluble solids in a device that rotates Separating butter from milk
at a very high speed
Soluble solids and liquids
Evaporation Used by exposing the components to the sun or by Separating sea salt from water
heating to get the solid component from the solid-
liquid homogeneous mixture
Used by selective evaporation and condensation
Distillation to get the liquid component from the solid-liquid Obtaining pure distilled water
homogeneous mixture
Crystallisation Used to obtain pure substance in the form of crystals Obtaining pure sugar crystals from a
sugar solution
45