Page 140 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 140
Basic Oxides
Basic oxides or metallic oxides are formed when metals react with oxygen on hea ng or without hea ng.
Some metallic oxides are given in Table 6.2.
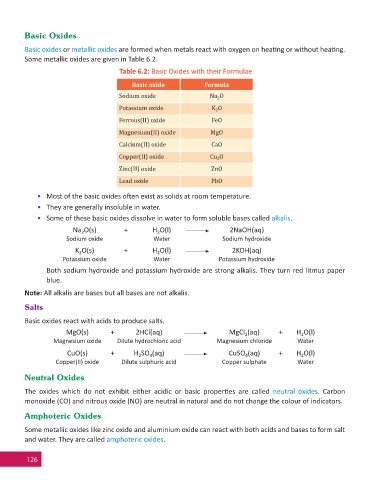
Table 6.2: Basic Oxides with their Formulae
Basic oxide Formula
Sodium oxide Na O
2
Potassium oxide K O
2
Ferrous(II) oxide FeO
Magnesium(II) oxide MgO
Calcium(II) oxide CaO
Copper(II) oxide Cu O
2
Zinc(II) oxide ZnO
Lead oxide PbO
• Most of the basic oxides o en exist as solids at room temperature.
• They are generally insoluble in water.
• Some of these basic oxides dissolve in water to form soluble bases called alkalis.
Na O(s) + H O(l) 2NaOH(aq)
2
2
Sodium oxide Water Sodium hydroxide
K O(s) + H O(l) 2KOH(aq)
2
2
Potassium oxide Water Potassium hydroxide
Both sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide are strong alkalis. They turn red litmus paper
blue.
Note: All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
Salts
Basic oxides react with acids to produce salts.
MgO(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl (aq) + H O(l)
2
2
Magnesium oxide Dilute hydrochloric acid Magnesium chloride Water
CuO(s) + H SO (aq) CuSO (aq) + H O(l)
4
2
2
4
Copper(II) oxide Dilute sulphuric acid Copper sulphate Water
Neutral Oxides
The oxides which do not exhibit either acidic or basic proper es are called neutral oxides. Carbon
monoxide (CO) and nitrous oxide (NO) are neutral in natural and do not change the colour of indicators.
Amphoteric Oxides
Some metallic oxides like zinc oxide and aluminium oxide can react with both acids and bases to form salt
and water. They are called amphoteric oxides.
126