Page 135 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 135
Heat
2Mg + O 2MgO
2
Magnesium Oxygen Magnesium oxide
We can see that magnesium gets oxidised with the addiƟ on of oxygen.
• Removal of hydrogen: Hydrogen sulphide reacts with chlorine and gets oxidised to sulphur due to
loss of hydrogen.
H S + Cl 2HCl + S
2
2
Hydrogen sulphide Chlorine Hydrochloric acid Sulphur
ReducƟ on: The addiƟ on of hydrogen or the removal of oxygen from a substance is called reducƟ on.
• AddiƟ on of hydrogen: Hydrogen reacts with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride.
H 2 + Cl 2HCl
2
Hydrogen Chlorine Hydrogen chloride
Since hydrogen is added to chlorine, it is a reducƟ on reacƟ on.
• Removal of oxygen: Copper oxide reacts with hydrogen to form copper by the removal of oxygen
from copper oxide.
Heat
CuO + H Cu + H O
2
2
Copper oxide Hydrogen Copper Water
Copper oxide is reduced to copper.
Oxidising and Reducing Agents
Oxidising agent: An atom or a group of atoms which accepts electrons during an oxidaƟ on reacƟ on is
called an oxidising agent. Some common oxidising agents are oxygen, ozone, chlorine, bromine, nitric acid
and sulphuric acid.
Reducing agent: An atom or a group of atoms which loses electrons during a chemical reacƟ on is called a
reducing agent. Some common reducing agents are hydrogen, carbon and sulphur dioxide.
Examples:
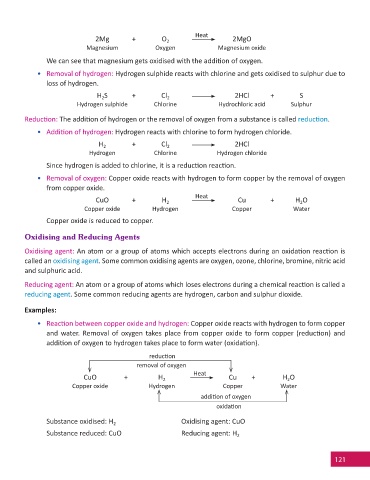
• ReacƟ on between copper oxide and hydrogen: Copper oxide reacts with hydrogen to form copper
and water. Removal of oxygen takes place from copper oxide to form copper (reducƟ on) and
addiƟ on of oxygen to hydrogen takes place to form water (oxidaƟ on).
reducƟ on
removal of oxygen
Heat
CuO + H Cu + H O
2
2
Copper oxide Hydrogen Copper Water
addiƟ on of oxygen
oxidaƟ on
Substance oxidised: H Oxidising agent: CuO
2
Substance reduced: CuO Reducing agent: H 2
121