Page 131 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 131
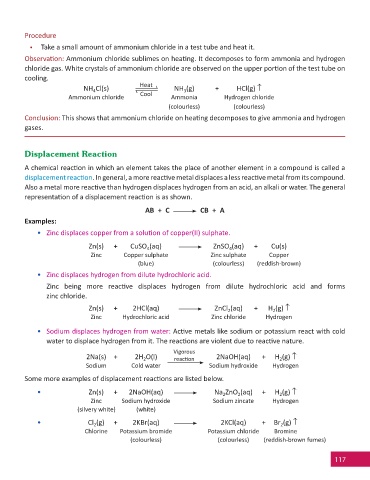
Procedure
• Take a small amount of ammonium chloride in a test tube and heat it.
Observa on: Ammonium chloride sublimes on hea ng. It decomposes to form ammonia and hydrogen
chloride gas. White crystals of ammonium chloride are observed on the upper por on of the test tube on
cooling.
Heat
NH Cl(s) NH (g) + HCl(g)
4
3
Ammonium chloride Cool Ammonia Hydrogen chloride
(colourless) (colourless)
Conclusion: This shows that ammonium chloride on hea ng decomposes to give ammonia and hydrogen
gases.
Displacement Reaction
A chemical reac on in which an element takes the place of another element in a compound is called a
displacement reac on. In general, a more reac ve metal displaces a less reac ve metal from its compound.
Also a metal more reac ve than hydrogen displaces hydrogen from an acid, an alkali or water. The general
representa on of a displacement reac on is as shown.
AB + C CB + A
Examples:
• Zinc displaces copper from a solu on of copper(II) sulphate.
Zn(s) + CuSO (aq) ZnSO (aq) + Cu(s)
4
4
Zinc Copper sulphate Zinc sulphate Copper
(blue) (colourless) (reddish-brown)
• Zinc displaces hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid.
Zinc being more reac ve displaces hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid and forms
zinc chloride.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl (aq) + H (g)
2
2
Zinc Hydrochloric acid Zinc chloride Hydrogen
• Sodium displaces hydrogen from water: Ac ve metals like sodium or potassium react with cold
water to displace hydrogen from it. The reac ons are violent due to reac ve nature.
Vigorous
2Na(s) + 2H O(l) reac on 2NaOH(aq) + H (g)
2
2
Sodium Cold water Sodium hydroxide Hydrogen
Some more examples of displacement reac ons are listed below.
• Zn(s) + 2NaOH(aq) Na ZnO (aq) + H (g)
2
2
2
Zinc Sodium hydroxide Sodium zincate Hydrogen
(silvery white) (white)
• Cl (g) + 2KBr(aq) 2KCl(aq) + Br (g)
2
2
Chlorine Potassium bromide Potassium chloride Bromine
(colourless) (colourless) (reddish-brown fumes)
117