Page 128 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 128
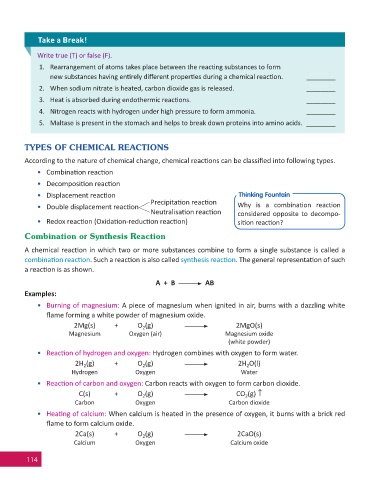
Take a Break!
Write true (T) or false (F).
1. Rearrangement of atoms takes place between the reac ng substances to form
new substances having en rely diff erent proper es during a chemical reac on. ________
2. When sodium nitrate is heated, carbon dioxide gas is released. ________
3. Heat is absorbed during endothermic reac ons. ________
4. Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen under high pressure to form ammonia. ________
5. Maltase is present in the stomach and helps to break down proteins into amino acids. ________
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
According to the nature of chemical change, chemical reac ons can be classifi ed into following types.
• Combina on reac on
• Decomposi on reac on
• Displacement reac on Thinking Fountain
Precipita on reac on
• Double displacement reac on Why is a combina on reac on
Neutralisa on reac on considered opposite to decompo-
• Redox reac on (Oxida on-reduc on reac on) si on reac on?
Combination or Synthesis Reaction
A chemical reac on in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance is called a
combina on reac on. Such a reac on is also called synthesis reac on. The general representa on of such
a reac on is as shown.
A + B AB
Examples:
• Burning of magnesium: A piece of magnesium when ignited in air, burns with a dazzling white
fl ame forming a white powder of magnesium oxide.
2Mg(s) + O (g) 2MgO(s)
2
Magnesium Oxygen (air) Magnesium oxide
(white powder)
• Reac on of hydrogen and oxygen: Hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water.
2H (g) + O (g) 2H O(l)
2
2
2
Hydrogen Oxygen Water
• Reac on of carbon and oxygen: Carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
C(s) + O (g) CO (g)
2
2
Carbon Oxygen Carbon dioxide
• Hea ng of calcium: When calcium is heated in the presence of oxygen, it burns with a brick red
fl ame to form calcium oxide.
2Ca(s) + O (g) 2CaO(s)
2
Calcium Oxygen Calcium oxide
114