Page 129 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 129
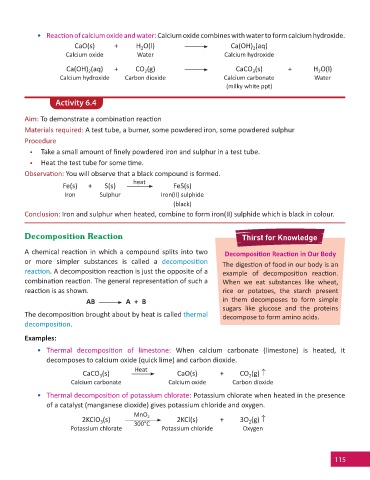
• Reac on of calcium oxide and water: Calcium oxide combines with water to form calcium hydroxide.
CaO(s) + H O(l) Ca(OH) (aq)
2
2
Calcium oxide Water Calcium hydroxide
Ca(OH) (aq) + CO (g) CaCO (s) + H O(l)
2
2
2
3
Calcium hydroxide Carbon dioxide Calcium carbonate Water
(milky white ppt)
Activity 6.4
Aim: To demonstrate a combina on reac on
Materials required: A test tube, a burner, some powdered iron, some powdered sulphur
Procedure
• Take a small amount of fi nely powdered iron and sulphur in a test tube.
• Heat the test tube for some me.
Observa on: You will observe that a black compound is formed.
heat
Fe(s) + S(s) FeS(s)
Iron Sulphur Iron(II) sulphide
(black)
Conclusion: Iron and sulphur when heated, combine to form iron(II) sulphide which is black in colour.
Decomposition Reaction Thirst for Knowledge
A chemical reac on in which a compound splits into two Decomposi on Reac on in Our Body
or more simpler substances is called a decomposi on
The diges on of food in our body is an
reac on. A decomposi on reac on is just the opposite of a example of decomposi on reac on.
combina on reac on. The general representa on of such a When we eat substances like wheat,
reac on is as shown. rice or potatoes, the starch present
AB A + B in them decomposes to form simple
sugars like glucose and the proteins
The decomposi on brought about by heat is called thermal decompose to form amino acids.
decomposi on.
Examples:
• Thermal decomposi on of limestone: When calcium carbonate (limestone) is heated, it
decomposes to calcium oxide (quick lime) and carbon dioxide.
Heat
CaCO (s) CaO(s) + CO (g)
2
3
Calcium carbonate Calcium oxide Carbon dioxide
• Thermal decomposi on of potassium chlorate: Potassium chlorate when heated in the presence
of a catalyst (manganese dioxide) gives potassium chloride and oxygen.
MnO
2KClO (s) 300°C 2 2KCl(s) + 3O (g)
3
2
Potassium chlorate Potassium chloride Oxygen
115