Page 111 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 111
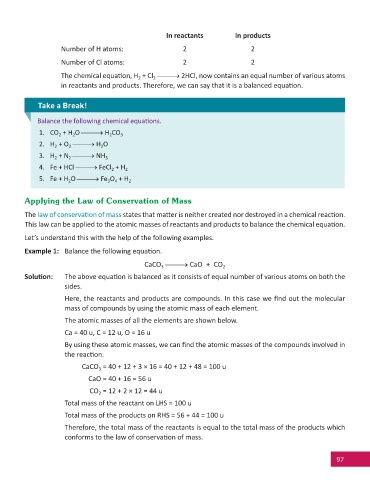
In reactants In products
Number of H atoms: 2 2
Number of Cl atoms: 2 2
The chemical equa on, H + Cl 2HCl, now contains an equal number of various atoms
2
2
in reactants and products. Therefore, we can say that it is a balanced equa on.
Take a Break!
Balance the following chemical equa ons.
1. CO + H O H CO 3
2
2
2
2. H + O H O
2
2
2
3. H + N NH 3
2
2
4. Fe + HCl FeCl + H 2
2
5. Fe + H O Fe O + H 2
4
3
2
Applying the Law of Conservation of Mass
The law of conserva on of mass states that ma er is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reac on.
This law can be applied to the atomic masses of reactants and products to balance the chemical equa on.
Let’s understand this with the help of the following examples.
Example 1: Balance the following equa on.
CaCO CaO + CO 2
3
Solu on: The above equa on is balanced as it consists of equal number of various atoms on both the
sides.
Here, the reactants and products are compounds. In this case we fi nd out the molecular
mass of compounds by using the atomic mass of each element.
The atomic masses of all the elements are shown below.
Ca = 40 u, C = 12 u, O = 16 u
By using these atomic masses, we can fi nd the atomic masses of the compounds involved in
the reac on.
CaCO = 40 + 12 + 3 × 16 = 40 + 12 + 48 = 100 u
3
CaO = 40 + 16 = 56 u
CO = 12 + 2 × 12 = 44 u
2
Total mass of the reactant on LHS = 100 u
Total mass of the products on RHS = 56 + 44 = 100 u
Therefore, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products which
conforms to the law of conserva on of mass.
97