Page 224 - Start Up Mathematics_8 (Non CCE)
P. 224
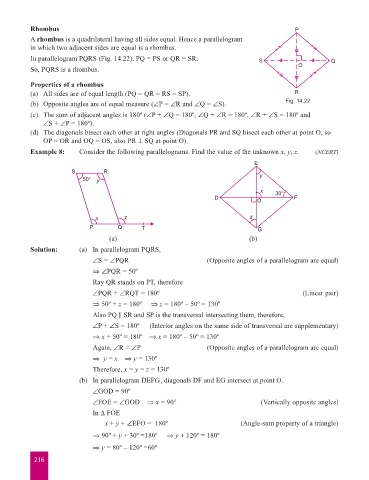
Rhombus P
A rhombus is a quadrilateral having all sides equal. Hence a parallelogram
in which two adjacent sides are equal is a rhombus.
In parallelogram PQRS (Fig. 14.22), PQ = PS or QR = SR. S Q
So, PQRS is a rhombus. O
Properties of a rhombus
(a) All sides are of equal length (PQ = QR = RS = SP). R
(b) Opposite angles are of equal measure (–P = –R and –Q = –S). Fig. 14.22
(c) The sum of adjacent angles is 180º (–P + –Q = 180º, –Q + –R = 180º, –R + –S = 180º and
–S + –P = 180º).
(d) The diagonals bisect each other at right angles (Diagonals PR and SQ bisect each other at point O, so
OP = OR and OQ = OS, also PR ^ SQ at point O).
Example 8: Consider the following parallelograms. Find the value of the unknown x, y, z. (NCERT)
E
S R
50° y y
x 30°
D O F
x z z
P Q T G
(a) (b)
Solution: (a) In parallelogram PQRS,
–S = –PQR (Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal)
fi –PQR = 50º
Ray QR stands on PT, therefore
–PQR + –RQT = 180º (Linear pair)
fi 50º + z = 180º fi z = 180º – 50º = 130º
Also PQ || SR and SP is the transversal intersecting them, therefore,
–P + –S = 180º (Interior angles on the same side of transversal are supplementary)
fi x + 50º = 180º fi x = 180º – 50º = 130º
Again, –R = –P (Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal)
fi y = x fi y = 130º
Therefore, x = y = z = 130º
(b) In parallelogram DEFG, diagonals DF and EG intersect at point O.
–GOD = 90º
–FOE = –GOD fi x = 90° (Vertically opposite angles)
In D FOE
x + y + –EFO = 180º (Angle-sum property of a triangle)
fi 90º + y + 30º = 180º fi y + 120º = 180º
fi y = 80º – 120º = 60º
216