Page 51 - ICSE Math 5
P. 51
Division of 3-Digit and 4-Digit Numbers by a 2-Digit Number
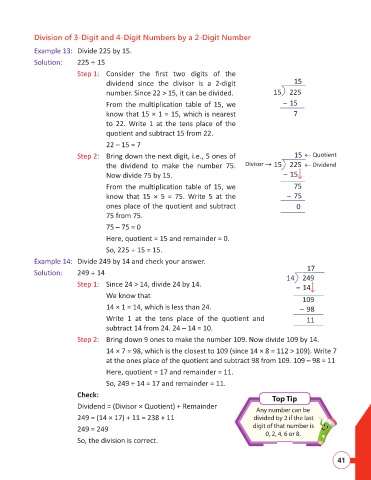
Example 13: Divide 225 by 15.
Solution: 225 15
Step 1: Consider the first two digits of the
dividend since the divisor is a 2-digit 15
number. Since 22 > 15, it can be divided. 15 225
From the multiplication table of 15, we – 15
know that 15 × 1 = 15, which is nearest 7
to 22. Write 1 at the tens place of the
quotient and subtract 15 from 22.
22 – 15 = 7
Step 2: Bring down the next digit, i.e., 5 ones of 15 Quotient
the dividend to make the number 75. Divisor 15 225 Dividend
Now divide 75 by 15. – 15
From the multiplication table of 15, we 75
know that 15 × 5 = 75. Write 5 at the – 75
ones place of the quotient and subtract 0
75 from 75.
75 – 75 = 0
Here, quotient = 15 and remainder = 0.
So, 225 15 = 15.
Example 14: Divide 249 by 14 and check your answer.
17
Solution: 249 14
14 249
Step 1: Since 24 > 14, divide 24 by 14.
– 14
We know that
109
14 × 1 = 14, which is less than 24. – 98
Write 1 at the tens place of the quotient and 11
subtract 14 from 24. 24 – 14 = 10.
Step 2: Bring down 9 ones to make the number 109. Now divide 109 by 14.
14 × 7 = 98, which is the closest to 109 (since 14 × 8 = 112 > 109). Write 7
at the ones place of the quotient and subtract 98 from 109. 109 – 98 = 11
Here, quotient = 17 and remainder = 11.
So, 249 ÷ 14 = 17 and remainder = 11.
Check:
Top Tip
Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
Any number can be
249 = (14 × 17) + 11 = 238 + 11 divided by 2 if the last
249 = 249 digit of that number is
0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.
So, the division is correct.
41