Page 100 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 100
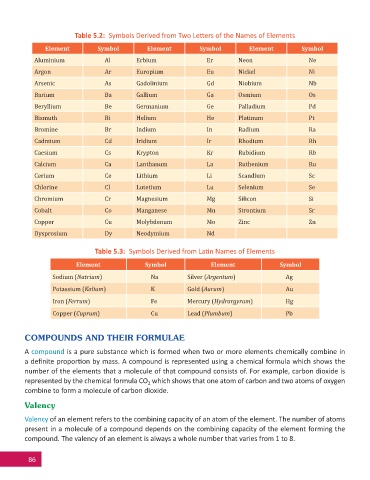
Table 5.2: Symbols Derived from Two Le ers of the Names of Elements
Element Symbol Element Symbol Element Symbol
Aluminium Al Erbium Er Neon Ne
Argon Ar Europium Eu Nickel Ni
Arsenic As Gadolinium Gd Niobium Nb
Barium Ba Gallium Ga Osmium Os
Beryllium Be Germanium Ge Palladium Pd
Bismuth Bi Helium He Platinum Pt
Bromine Br Indium In Radium Ra
Cadmium Cd Iridium Ir Rhodium Rh
Caesium Cs Krypton Kr Rubidium Rb
Calcium Ca Lanthanum La Ruthenium Ru
Cerium Ce Lithium Li Scandium Sc
Chlorine Cl Lutetium Lu Selenium Se
Chromium Cr Magnesium Mg Silicon Si
Cobalt Co Manganese Mn Strontium Sr
Copper Cu Molybdenum Mo Zinc Zn
Dysprosium Dy Neodymium Nd
Table 5.3: Symbols Derived from La n Names of Elements
Element Symbol Element Symbol
Sodium (Natrium) Na Silver (Argentum) Ag
Potassium (Kalium) K Gold (Aurum) Au
Iron (Ferrum) Fe Mercury (Hydrargyrum) Hg
Copper (Cuprum) Cu Lead (Plumbum) Pb
COMPOUNDS AND THEIR FORMULAE
A compound is a pure substance which is formed when two or more elements chemically combine in
a defi nite propor on by mass. A compound is represented using a chemical formula which shows the
number of the elements that a molecule of that compound consists of. For example, carbon dioxide is
represented by the chemical formula CO which shows that one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen
2
combine to form a molecule of carbon dioxide.
Valency
Valency of an element refers to the combining capacity of an atom of the element. The number of atoms
present in a molecule of a compound depends on the combining capacity of the element forming the
compound. The valency of an element is always a whole number that varies from 1 to 8.
86