Page 22 - Start Up Mathematics_8 (Non CCE)
P. 22
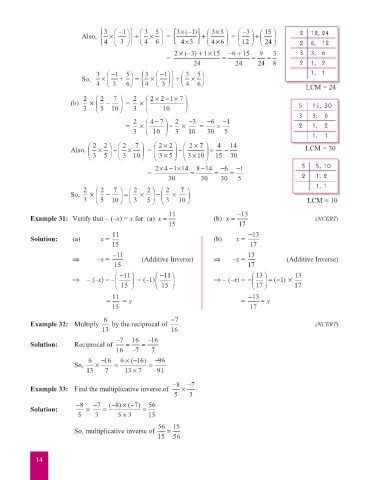
3 − 1 3 5 { 3×−() 35× 3 15 2 12, 24
1
−
+
Also, × + × = } = +
×
4 3 4 6 43× 46 12 24 2 6, 12
2 ×−( 3 +×) 115 −+ 9 3 3 3, 6
615
= = = =
24 24 24 8 2 1, 2
3 − 1 5 3 − 1 3 5 1, 1
So, × + = × + ×
4 3 6 4 3 4 6 LCM = 24
2 2 7 2 22 17
×− ×
(b) × − = ×
3 5 10 3 10 5 15, 30
3 3, 6
2 47− 2 − 3 −6 −1
= × = × = = 2 1, 2
3 10 3 10 30 5 1, 1
×
2 2 2 7 22× 27 4 14
Also, × × = = − LCM = 30
−
−
×
3 5 3 10 35× 310 15 30
×− ×
24 114 814− − 6 − 1 5 5, 10
= = = =
30 30 30 5 2 1, 2
1, 1
2 2 7 2 2 2 7
−
=
So, × − × ×
3 5 10 3 5 3 10 LCM = 10
11 −13
Example 31: Verify that – (–x) = x for: (a) x = (b) x = (NCERT)
15 17
11 −13
Solution: (a) x = (b) x =
15 17
−11 13
⇒ –x = (Additive Inverse) ⇒ –x = (Additive Inverse)
15 17
−11 −11 13 13
⇒ – (–x) = – = (–1) ⇒ – (–x) = − =−1() ×
15 15 17 17
11 −13
= = x = = x
15 17
6 −7
Example 32: Multiply by the reciprocal of . (NCERT)
13 16
−7 16 −16
Solution: Reciprocal of = =
16 −7 7
6 − 16 6 ×−( 16) − 96
So, × = =
13 7 13 7× 91
−8 −7
Example 33: Find the multiplicative inverse of × .
5 3
−8 −7 ( −8) × −7( ) 56
Solution: × = =
5 3 53 15
×
56 15
So, multiplicative inverse of =
15 56
14