Page 196 - ICSE Math 6
P. 196
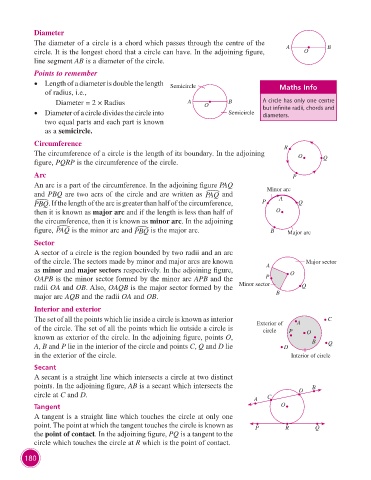
Diameter
The diameter of a circle is a chord which passes through the centre of the
circle. It is the longest chord that a circle can have. In the adjoining figure, A O B
line segment AB is a diameter of the circle.
Points to remember
• Length of a diameter is double the length Semicircle Maths Info
of radius, i.e.,
Diameter = 2 × Radius A O B A circle has only one centre
• Diameter of a circle divides the circle into Semicircle but infinite radii, chords and
diameters.
two equal parts and each part is known
as a semicircle.
Circumference R
The circumference of a circle is the length of its boundary. In the adjoining O
figure, PQRP is the circumference of the circle. Q
Arc P
An arc is a part of the circumference. In the adjoining figure PAQ
and PBQ are two acrs of the circle and are written as PAQ and Minor arc
A
PBQ. If the length of the arc is greater than half of the circumference, P Q
then it is known as major arc and if the length is less than half of O
the circumference, then it is known as minor arc. In the adjoining
figure, PAQ is the minor arc and PBQ is the major arc. B Major arc
Sector
A sector of a circle is the region bounded by two radii and an arc
of the circle. The sectors made by minor and major arcs are known Major sector
as minor and major sectors respectively. In the adjoining figure, A O
OAPB is the minor sector formed by the minor arc APB and the P
radii OA and OB. Also, OAQB is the major sector formed by the Minor sector Q
major arc AQB and the radii OA and OB. B
Interior and exterior
The set of all the points which lie inside a circle is known as interior A C
of the circle. The set of all the points which lie outside a circle is Exterior of P O
circle
known as exterior of the circle. In the adjoining figure, points O,
A, B and P lie in the interior of the circle and points C, Q and D lie D B Q
in the exterior of the circle. Interior of circle
Secant
A secant is a straight line which intersects a circle at two distinct
points. In the adjoining figure, AB is a secant which intersects the B
circle at C and D. C D
A
Tangent O
A tangent is a straight line which touches the circle at only one
point. The point at which the tangent touches the circle is known as P R Q
the point of contact. In the adjoining figure, PQ is a tangent to the
circle which touches the circle at R which is the point of contact.
180