Page 140 - ICSE GEOGRAPHY
P. 140
training facilities, and lack of health and availability of water resources attracts
medical facilities are some of the problems a large agrarian population. Hence, the
that people in rural India face. To get rid of largest concentration of population occurs
these issues and to have better opportunities in the plains of the north, particularly in
in life, rural populations migrate to urban the Ganga Plain.
areas. Hence, the population distribution • India’s geography and weather are diverse.
changes which results in an increase in urban Th e coastal areas and the cities that are
population. near large water bodies also attract a
large population due to their favourable
Benefi ts of Urban Life
climatic conditions. On the other hand,
Urban life has its own benefi ts such as better
the western region of India that makes up
educational, medical and health facilities,
the Th ar Desert, is sparsely populated as a
greater number of job opportunities, better
result of its harsh climate.
developed modes of transport and recreation
• Th e relief features also play a vital role
centres. People from villages get lured by these
in the distribution of population. Plains
materialistic services and try to settle down in
have more scope for modern development
towns and cities. Th e National Sample Survey
as compared to hills, deserts or marshy
Organisation states that the main reason a
lands and can provide latest infrastructural
rural male migrates to an urban area is for
benefi ts such as convenient transportation.
employment whereas a rural female does so
Srinagar Valley, Delhi, Pune and Nasik are
for matrimonial reasons.
all well-connected by roadways or railways.
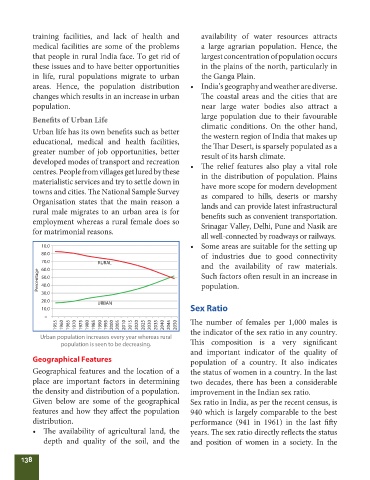
10.0 • Some areas are suitable for the setting up
80.0
of industries due to good connectivity
70.0 RURAL and the availability of raw materials.
60.0
Percentage 50.0 Such factors oft en result in an increase in
40.0
population.
30.0
20.0
URBAN
10.0 Sex Ratio
–
1955 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040 2045 2050 Th e number of females per 1,000 males is
the indicator of the sex ratio in any country.
Urban population increases every year whereas rural
population is seen to be decreasing. Th is composition is a very signifi cant
and important indicator of the quality of
Geographical Features population of a country. It also indicates
Geographical features and the location of a the status of women in a country. In the last
place are important factors in determining two decades, there has been a considerable
the density and distribution of a population. improvement in the Indian sex ratio.
Given below are some of the geographical Sex ratio in India, as per the recent census, is
features and how they aff ect the population 940 which is largely comparable to the best
distribution. performance (941 in 1961) in the last fi ft y
• Th e availability of agricultural land, the years. Th e sex ratio directly refl ects the status
depth and quality of the soil, and the and position of women in a society. In the
138