Page 209 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 209
Coal
Coal is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and some free carbon. Small amounts of nitrogen and sulphur
compounds are also present in coal. It is found in deep mines under the surface of earth. It is a combus ble
compact black or dark-brown sedimentary rock.
Formation of Coal
Coal is formed by the decomposi on of ancient plants buried Thirst for Knowledge
under the earth millions of years ago. It is believed that dead
plants were covered by rocks and soil and were decomposed Carbonisa on is a slow process
by bacteria. New plants grew in the soil and they too got buried and may have taken thousand of
years to convert decayed plant
under the soil and rocks. Volcanic erup ons and earthquakes
ma er into coal.
destroyed forests which also got buried under the surface of the
earth and got covered with sand, clay and water. Over the years,
these remains went deeper and deeper inside the earth. Due to high temperature and pressure inside
the earth’s surface and in the absence of air they got converted into coal. The slow chemical process of
conversion of dead and decaying ma er into coal is called carbonisa on.
Coal is mainly carbon as plants contain carbon compounds but the carbon content varies in diff erent
types of coal.
Types of Coal
There are four varie es of coal which diff er in their carbon content.
1. Peat 2. Lignite 3. Bituminous 4. Anthracite
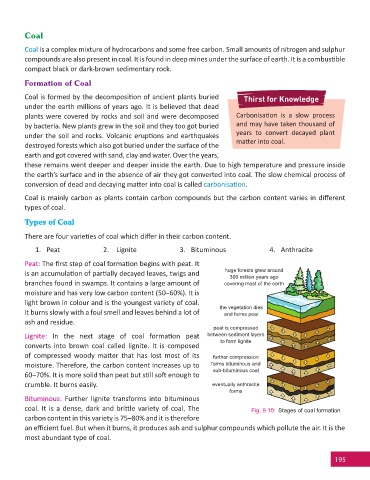
Peat: The fi rst step of coal forma on begins with peat. It
huge forests grew around w around
is an accumula on of par ally decayed leaves, twigs and
rs ago
300 million years ago
branches found in swamps. It contains a large amount of covering most of the earth
he earth
moisture and has very low carbon content (50–60%). It is
light brown in colour and is the youngest variety of coal.
the vegetation dies
It burns slowly with a foul smell and leaves behind a lot of and forms peat
ash and residue.
peat is compressed
Lignite: In the next stage of coal forma on peat between sediment layers
to form lignite
converts into brown coal called lignite. It is composed
of compressed woody ma er that has lost most of its further compression
moisture. Therefore, the carbon content increases up to forms bituminous and
sub-bituminous coal
60–70%. It is more solid than peat but s ll so enough to
crumble. It burns easily. eventually anthracite
forms
Bituminous: Further lignite transforms into bituminous
coal. It is a dense, dark and bri le variety of coal. The Fig. 9.10: Stages of coal formation
carbon content in this variety is 75–80% and it is therefore
an effi cient fuel. But when it burns, it produces ash and sulphur compounds which pollute the air. It is the
most abundant type of coal.
195