Page 286 - ICSE Math 8
P. 286
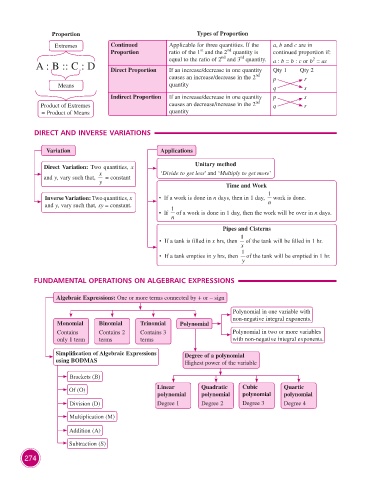
Proportion Types of Proportion
Extremes Continued Applicable for three quantities. If the a, b and c are in
st
nd
Proportion ratio of the 1 and the 2 quantity is continued proportion if:
rd
nd
2
A : B :: C : D Direct Proportion equal to the ratio of 2 and 3 quantity. a : b = b : c or b = ac
Qty 1 Qty 2
If an increase/decrease in one quantity
nd
causes an increase/decrease in the 2 p r
Means quantity q s
Indirect Proportion If an increase/decrease in one quantity p s
nd
Product of Extremes causes an decrease/increase in the 2 q r
= Product of Means quantity
DIRECT AND INVERSE VARIATIONS
Variation Applications
Direct Variation: Two quantities, x Unitary method
x ‘Divide to get less’ and ‘Multiply to get more’
and y, vary such that, = constant
y
Time and Work
1
Inverse Variation: Two quantities, x • If a work is done in n days, then in 1 day, work is done.
and y, vary such that, xy = constant. 1 n
• If of a work is done in 1 day, then the work will be over in n days.
n
Pipes and Cisterns
1
• If a tank is filled in x hrs, then of the tank will be filled in 1 hr.
x
1
• If a tank empties in y hrs, then of the tank will be emptied in 1 hr.
y
FUNDAMENTAL OPERATIONS ON ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
Algebraic Expressions: One or more terms connected by + or – sign
Polynomial in one variable with
non-negative integral exponents.
Monomial Binomial Trinomial Polynomial
Contains Contains 2 Contains 3 Polynomial in two or more variables
only 1 term terms terms with non-negative integral exponents.
Simplification of Algebraic Expressions Degree of a polynomial
using BODMAS Highest power of the variable
Brackets (B)
Of (O) Linear Quadratic Cubic Quartic
polynomial polynomial polynomial polynomial
Division (D) Degree 1 Degree 2 Degree 3 Degree 4
Multiplication (M)
Addition (A)
Subtraction (S)
274