Page 285 - ICSE Math 8
P. 285
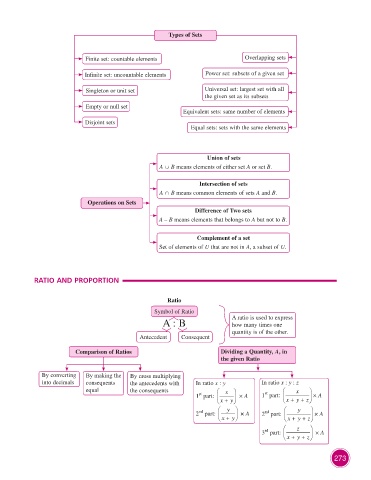
Types of Sets
Finite set: countable elements Overlapping sets
Infinite set: uncountable elements Power set: subsets of a given set
Singleton or unit set Universal set: largest set with all
the given set as its subsets
Empty or null set
Equivalent sets: same number of elements
Disjoint sets
Equal sets: sets with the same elements
Union of sets
A ∪ B means elements of either set A or set B.
Intersection of sets
A ∩ B means common elements of sets A and B.
Operations on Sets
Difference of Two sets
A – B means elements that belongs to A but not to B.
Complement of a set
Set of elements of U that are not in A, a subset of U.
RATIO AND PROPORTION
Ratio
Symbol of Ratio
A : B A ratio is used to express
how many times one
quantity is of the other.
Antecedent Consequent
Comparison of Ratios Dividing a Quantity, A, in
the given Ratio
By converting By making the By cross multiplying
into decimals consequents the antecedents with In ratio x : y In ratio x : y : z
equal the consequents x x
st
1 part: × A 1 part: st × A
x + y x + y + z
nd y nd y
2 part: × A 2 part: × A
x + y x + y + z
z
3 part: rd × A
x + y + z
273