Page 188 - ICSE Math 8
P. 188
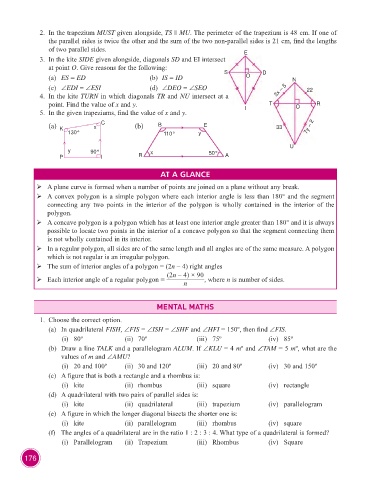
2. In the trapezium MUST given alongside, TS || MU. The perimeter of the trapezium is 48 cm. If one of
the parallel sides is twice the other and the sum of the two non-parallel sides is 21 cm, find the lengths
of two parallel sides.
E
3. In the kite SIDE given alongside, diagonals SD and EI intersect
at point O. Give reasons for the following: S
(a) ES = ED (b) IS = ID O D N
(c) ∠EDI = ∠ESI (d) ∠DEO = ∠SEO 3x – 5 22
4. In the kite TURN in which diagonals TR and NU intersect at a
point. Find the value of x and y. I T O R
5. In the given trapeziums, find the value of x and y.
(a) K x C (b) B E 33 7y – 2
130° 110° y
U
y 90° x 50°
P I R A
AT A GLANCE
¾ A plane curve is formed when a number of points are joined on a plane without any break.
¾ A convex polygon is a simple polygon where each interior angle is less than 180° and the segment
connecting any two points in the interior of the polygon is wholly contained in the interior of the
polygon.
¾ A concave polygon is a polygon which has at least one interior angle greater than 180° and it is always
possible to locate two points in the interior of a concave polygon so that the segment connecting them
is not wholly contained in its interior.
¾ In a regular polygon, all sides are of the same length and all angles are of the same measure. A polygon
which is not regular is an irregular polygon.
¾ The sum of interior angles of a polygon = (2n – 4) right angles
(2n – 4) × 90
¾ Each interior angle of a regular polygon = , where n is number of sides.
n
MENTAL MATHS
1. Choose the correct option.
(a) In quadrilateral FISH, –FIS = –ISH = –SHF and –HFI = 150º, then find –FIS.
(i) 80º (ii) 70º (iii) 75º (iv) 85º
(b) Draw a line TALK and a parallelogram ALUM. If –KLU = 4 mº and –TAM = 5 mº, what are the
values of m and –AMU?
(i) 20 and 100º (ii) 30 and 120º (iii) 20 and 80º (iv) 30 and 150º
(c) A figure that is both a rectangle and a rhombus is:
(i) kite (ii) rhombus (iii) square (iv) rectangle
(d) A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides is:
(i) kite (ii) quadrilateral (iii) trapezium (iv) parallelogram
(e) A figure in which the longer diagonal bisects the shorter one is:
(i) kite (ii) parallelogram (iii) rhombus (iv) square
(f) The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 : 4. What type of a quadrilateral is formed?
(i) Parallelogram (ii) Trapezium (iii) Rhombus (iv) Square
176