Page 194 - ICSE Math 5
P. 194
5. Represent the given information using tally marks.
(a) Marks in Number of (b) Number of
Type of Chocolate
Mathematics Students Children
Below 30 4 Milk chocolate 25
30 to 40 7 Almond chocolate 20
40 to 50 9 Fruit and nut
50 to 60 8 chocolate 21
60 to 70 12 Cashew chocolate 30
70 to 80 5 Resin chocolate 32
Bar Graph
We know that in a bar graph, data is represented in the form of rectangular bars of different
heights but equal width. Bar graphs may be horizontal or vertical. We already know how to
interpret a bar graph. Now let’s learn to draw bar graphs.
We follow the given rules to draw a bar graph.
• Choose a suitable scale for the graph depending on the size of paper on which it needs to
be drawn.
• Draw two lines perpendicular to each other. Then label the horizontal and vertical lines as
X-axis and Y-axis, respectively.
• Draw rectangular bars of equal width to represent the values given in the data.
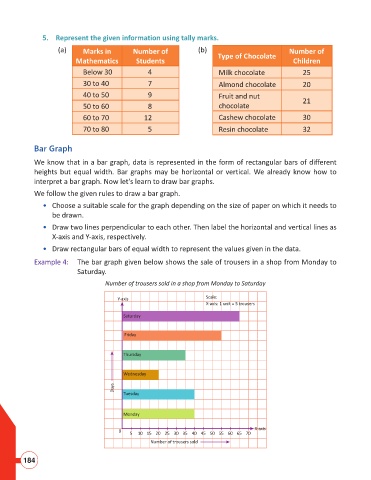
Example 4: The bar graph given below shows the sale of trousers in a shop from Monday to
Saturday.
Number of trousers sold in a shop from Monday to Saturday
Y-axis Scale:
X-axis: 1 unit = 5 trousers
Saturday
Friday
Thursday
Wednesday
Days
Tuesday
Monday
X-axis
0
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70
Number of trousers sold
184