Page 16 - Start Up Mathematics_8 (Non CCE)
P. 16
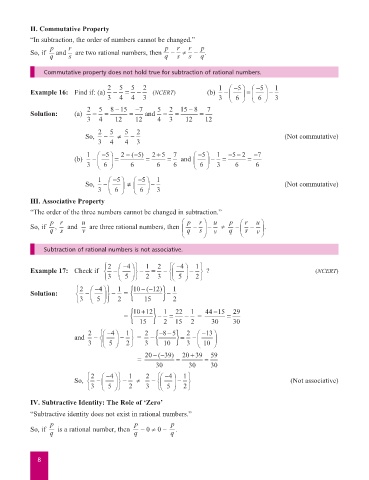
II. Commutative Property
“In subtraction, the order of numbers cannot be changed.”
p r p r r p
So, if q and s are two rational numbers, then q − ≠ − q .
s
s
Commutative property does not hold true for subtraction of rational numbers.
2 5 5 2 1 − 5 − 5 1
Example 16: Find if: (a) − = − (NCERT) (b) − −
=
3 4 4 3 3 6 6 3
2 5 815− − 7 5 2 15 8− 7
Solution: (a) − = = and − = =
3 4 12 12 4 3 12 12
2 5 5 2
So, − ≠ − (Not commutative)
3 4 4 3
1 − 5 2 −−( 5) 25+ 7 5 1 −−52 −7
−
(b) − = = = and − = =
3 6 6 6 6 6 3 6 6
1 − 5 5 1
−
So, − ≠ − (Not commutative)
3 6 6 3
III. Associative Property
“The order of the three numbers cannot be changed in subtraction.”
p r u p r u p r u
So, if , and are three rational numbers, then − − ≠ − − .
q s v q s v q s v
Subtraction of rational numbers is not associative.
2 − 4 1 2 − 4 1
Example 17: Check if − − = − − ? (NCERT)
3 5 2 3 5 2
2 − 4 1 { 10 −− ( 12) } 1
Solution: − − = −
3 5 2 15 2
{ 10 12+ } 1 22 1 44 15− 29
= 15 − 2 = 15 − 2 = 30 = 30
−−
2 − 4 1 2 { } 2 − 13
85
and − − = − = −
3 5 2 3 10 3 10
20 −−( 39) 20 39+ 59
= = =
30 30 30
2 − 4 1 2 − 4 1
So, − − ≠ − − (Not associative)
3 5 2 3 5 2
IV. Subtractive Identity: The Role of ‘Zero’
“Subtractive identity does not exist in rational numbers.”
p p p
So, if q is a rational number, then q – 0 ≠ 0 – q .
8