Page 199 - Start Up Mathematics_7
P. 199
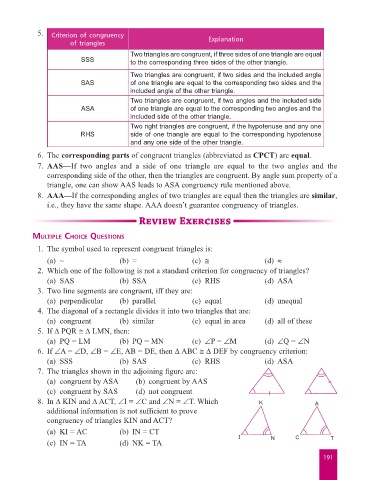
5. Criterion of congruency
of triangles Explanation
Two triangles are congruent, if three sides of one triangle are equal
SSS to the corresponding three sides of the other triangle.
Two triangles are congruent, if two sides and the included angle
SAS of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two sides and the
included angle of the other triangle.
Two triangles are congruent, if two angles and the included side
ASA of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two angles and the
included side of the other triangle.
Two right triangles are congruent, if the hypotenuse and any one
RHS side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse
and any one side of the other triangle.
6. The corresponding parts of congruent triangles (abbreviated as CPCT) are equal.
7. AAS—If two angles and a side of one triangle are equal to the two angles and the
corresponding side of the other, then the triangles are congruent. By angle sum property of a
triangle, one can show AAS leads to ASA congruency rule mentioned above.
8. AAA—If the corresponding angles of two triangles are equal then the triangles are similar,
i.e., they have the same shape. AAA doesn’t guarantee congruency of triangles.
Review Exercises
Multiple ChoiCe Questions
1. The symbol used to represent congruent triangles is:
(a) ~ (b) = (c) ≅ (d) ≈
2. Which one of the following is not a standard criterion for congruency of triangles?
(a) SAS (b) SSA (c) RHS (d) ASA
3. Two line segments are congruent, iff they are:
(a) perpendicular (b) parallel (c) equal (d) unequal
4. The diagonal of a rectangle divides it into two triangles that are:
(a) congruent (b) similar (c) equal in area (d) all of these
5. If ∆ PQR ≅ ∆ LMN, then:
(a) PQ = LM (b) PQ = MN (c) ∠P = ∠M (d) ∠Q = ∠N
6. If ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E, AB = DE, then ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ DEF by congruency criterion:
(a) SSS (b) SAS (c) RHS (d) ASA
7. The triangles shown in the adjoining figure are:
(a) congruent by ASA (b) congruent by AAS
(c) congruent by SAS (d) not congruent
8. In ∆ KIN and ∆ ACT, ∠I = ∠C and ∠N = ∠T. Which K A
additional information is not sufficient to prove
congruency of triangles KIN and ACT?
(a) KI = AC (b) IN = CT
I N C T
(c) IN = TA (d) NK = TA
191