Page 349 - Start Up Mathematics_8 (Non CCE)
P. 349
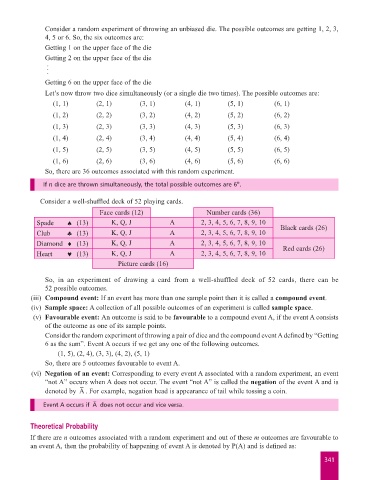
Consider a random experiment of throwing an unbiased die. The possible outcomes are getting 1, 2, 3,
4, 5 or 6. So, the six outcomes are:
Getting 1 on the upper face of the die
Getting 2 on the upper face of the die
.
.
.
Getting 6 on the upper face of the die
Let’s now throw two dice simultaneously (or a single die two times). The possible outcomes are:
(1, 1) (2, 1) (3, 1) (4, 1) (5, 1) (6, 1)
(1, 2) (2, 2) (3, 2) (4, 2) (5, 2) (6, 2)
(1, 3) (2, 3) (3, 3) (4, 3) (5, 3) (6, 3)
(1, 4) (2, 4) (3, 4) (4, 4) (5, 4) (6, 4)
(1, 5) (2, 5) (3, 5) (4, 5) (5, 5) (6, 5)
(1, 6) (2, 6) (3, 6) (4, 6) (5, 6) (6, 6)
So, there are 36 outcomes associated with this random experiment.
n
If n dice are thrown simultaneously, the total possible outcomes are 6 .
Consider a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing cards.
Face cards (12) Number cards (36)
Spade ™ (13) K, Q, J A 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 Black cards (26)
Club ß (13) K, Q, J A 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Diamond ® (13) K, Q, J A 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 Red cards (26)
Heart © (13) K, Q, J A 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
Picture cards (16)
So, in an experiment of drawing a card from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, there can be
52 possible outcomes.
(iii) Compound event: If an event has more than one sample point then it is called a compound event.
(iv) Sample space: A collection of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called sample space.
(v) Favourable event: An outcome is said to be favourable to a compound event A, if the event A consists
of the outcome as one of its sample points.
Consider the random experiment of throwing a pair of dice and the compound event A defined by “Getting
6 as the sum”. Event A occurs if we get any one of the following outcomes.
(1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 3), (4, 2), (5, 1)
So, there are 5 outcomes favourable to event A.
(vi) Negation of an event: Corresponding to every event A associated with a random experiment, an event
“not A” occurs when A does not occur. The event “not A” is called the negation of the event A and is
denoted by A . For example, negation head is appearance of tail while tossing a coin.
Event A occurs if A does not occur and vice versa.
Theoretical Probability
If there are n outcomes associated with a random experiment and out of these m outcomes are favourable to
an event A, then the probability of happening of event A is denoted by P(A) and is defined as:
341