Page 202 - ICSE Math 6
P. 202
19 Three-dimensional Shapes
Key Concepts
• Classification of Objects: 1D, 2D and 3D • Nets of 3D Shapes
• Elements of a 3D Shape - Faces, Edges and Vertices • Visualizing Solid Objects
• 3D Shapes: Cube, Cuboid, Cylinder, Cone, Sphere,
Prism, Pyramid
There are many objects around us. Some of them have only length (like a thread and a hair), some
have both length and breadth (like a sheet of paper), and some have length, breadth and height (like
an almirah). Thus we classify the objects around us into three broad categories; one-dimensional
(1D) objects (having only length), two-dimensional (2D) objects (having both length and breadth),
and three-dimensional (3D) objects (having length, breadth and height). In this chapter we will learn
about 3D shapes and objects.
Components of a 3D Shape
The components of a 3D shape are;
Face (F): The surface of a three-dimensional shape is called its face.
Edge (E): The line segment where the faces meet is called an edge.
Vertex (V): The corner where two edges intersect is called a vertex.
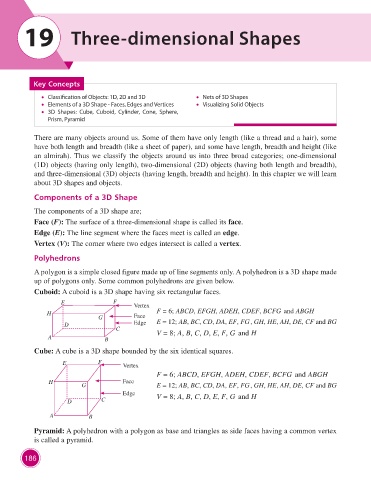
Polyhedrons
A polygon is a simple closed figure made up of line segments only. A polyhedron is a 3D shape made
up of polygons only. Some common polyhedrons are given below.
Cuboid: A cuboid is a 3D shape having six rectangular faces.
E F Vertex
H F = 6; ABCD, EFGH, ADEH, CDEF, BCFG and ABGH
G Face
D Edge E = 12; AB, BC, CD, DA, EF, FG, GH, HE, AH, DE, CF and BG
C V = 8; A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H
A B
Cube: A cube is a 3D shape bounded by the six identical squares.
E F Vertex
F = 6; ABCD, EFGH, ADEH, CDEF, BCFG and ABGH
H G Face E = 12; AB, BC, CD, DA, EF, FG, GH, HE, AH, DE, CF and BG
Edge V = 8; A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H
D C
A B
Pyramid: A polyhedron with a polygon as base and triangles as side faces having a common vertex
is called a pyramid.
186