Page 164 - ICSE Math 6
P. 164
15 Angles
Key Concepts
• Angle–Vertex, Arm, Naming, Interior and Exterior, • Special Pairs of Angles
Magnitude • Measurement of a Line Segment
• Types of Angles • Measurement of an Angle
• Special Angles • Construction of an Angle using Protractor
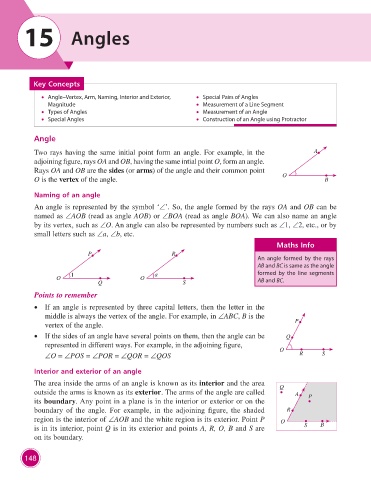
Angle
Two rays having the same initial point form an angle. For example, in the A
adjoining figure, rays OA and OB, having the same intial point O, form an angle.
Rays OA and OB are the sides (or arms) of the angle and their common point
O is the vertex of the angle. O B
Naming of an angle
An angle is represented by the symbol ‘∠’. So, the angle formed by the rays OA and OB can be
named as ∠AOB (read as angle AOB) or ∠BOA (read as angle BOA). We can also name an angle
by its vertex, such as ∠O. An angle can also be represented by numbers such as ∠1, ∠2, etc., or by
small letters such as ∠a, ∠b, etc.
Maths Info
P R
An angle formed by the rays
AB and BC is same as the angle
O 1 O a formed by the line segments
AB and BC.
Q S
Points to remember
• If an angle is represented by three capital letters, then the letter in the
middle is always the vertex of the angle. For example, in ∠ABC, B is the
vertex of the angle. P
• If the sides of an angle have several points on them, then the angle can be Q
represented in different ways. For example, in the adjoining figure,
∠O = ∠POS = ∠POR = ∠QOR = ∠QOS O R S
Interior and exterior of an angle
The area inside the arms of an angle is known as its interior and the area
outside the arms is known as its exterior. The arms of the angle are called Q A
its boundary. Any point in a plane is in the interior or exterior or on the P
boundary of the angle. For example, in the adjoining figure, the shaded R
region is the interior of ∠AOB and the white region is its exterior. Point P O
is in its interior, point Q is in its exterior and points A, R, O, B and S are S B
on its boundary.
148