Page 112 - Viva ICSE Computer Studies 8 : E-book
P. 112
Protocols
A set of rules that determines how the data should be transferred over networks (compressed,
presented and so on) is known as protocol. Let’s learn about diff erent types of protocols.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TCP/IP is an abbreviation of two Internet protocols—Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
and Internet Protocol (IP). TCP permits two Internet connected computers to get a reliable
connection, while IP is responsible for routing the data packets to a desired destination IP
address.
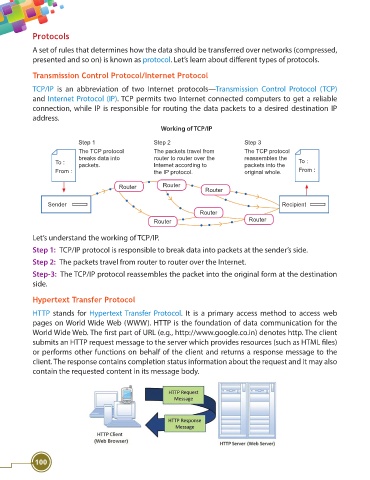
Working of TCP/IP
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
The TCP protocol The packets travel from The TCP protocol
breaks data into router to router over the reassembles the
To : To :
packets. Internet according to packets into the
From : the IP protocol. original whole. From :
Router Router
Router
Sender Recipient
Router
Router Router
Let’s understand the working of TCP/IP.
Step 1: TCP/IP protocol is responsible to break data into packets at the sender’s side.
Step 2: The packets travel from router to router over the Internet.
Step-3: The TCP/IP protocol reassembles the packet into the original form at the destination
side.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is a primary access method to access web
pages on World Wide Web (WWW). HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the
World Wide Web. The fi rst part of URL (e.g., http://www.google.co.in) denotes http. The client
submits an HTTP request message to the server which provides resources (such as HTML fi les)
or performs other functions on behalf of the client and returns a response message to the
client. The response contains completion status information about the request and it may also
contain the requested content in its message body.
100