Page 186 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 186
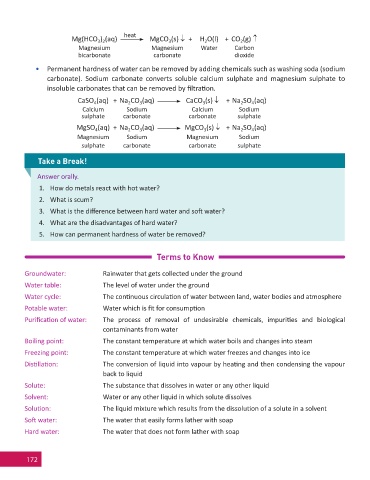
heat
Mg(HCO ) (aq) MgCO (s) + H O(l) + CO (g)
2
3 2
3
2
Magnesium Magnesium Water Carbon
bicarbonate carbonate dioxide
• Permanent hardness of water can be removed by adding chemicals such as washing soda (sodium
carbonate). Sodium carbonate converts soluble calcium sulphate and magnesium sulphate to
insoluble carbonates that can be removed by fi ltra on.
CaSO (aq) + Na CO (aq) CaCO (s) + Na SO (aq)
4
4
2
3
2
3
Calcium Sodium Calcium Sodium
sulphate carbonate carbonate sulphate
MgSO (aq) + Na CO (aq) MgCO (s) + Na SO (aq)
3
3
2
4
4
2
Magnesium Sodium Magnesium Sodium
sulphate carbonate carbonate sulphate
Take a Break!
Answer orally.
1. How do metals react with hot water?
2. What is scum?
3. What is the diff erence between hard water and so water?
4. What are the disadvantages of hard water?
5. How can permanent hardness of water be removed?
Terms to Know
Groundwater: Rainwater that gets collected under the ground
Water table: The level of water under the ground
Water cycle: The con nuous circula on of water between land, water bodies and atmosphere
Potable water: Water which is fi t for consump on
Purifi ca on of water: The process of removal of undesirable chemicals, impuri es and biological
contaminants from water
Boiling point: The constant temperature at which water boils and changes into steam
Freezing point: The constant temperature at which water freezes and changes into ice
Dis lla on: The conversion of liquid into vapour by hea ng and then condensing the vapour
back to liquid
Solute: The substance that dissolves in water or any other liquid
Solvent: Water or any other liquid in which solute dissolves
Solu on: The liquid mixture which results from the dissolu on of a solute in a solvent
So water: The water that easily forms lather with soap
Hard water: The water that does not form lather with soap
172