Page 160 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 160
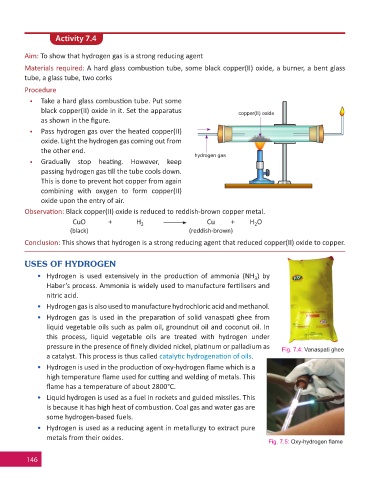
Activity 7.4
Aim: To show that hydrogen gas is a strong reducing agent
Materials required: A hard glass combus on tube, some black copper(II) oxide, a burner, a bent glass
tube, a glass tube, two corks
Procedure
• Take a hard glass combus on tube. Put some
black copper(II) oxide in it. Set the apparatus copper(II) oxide
as shown in the fi gure.
• Pass hydrogen gas over the heated copper(II)
oxide. Light the hydrogen gas coming out from
the other end.
hydrogen gas
• Gradually stop hea ng. However, keep
passing hydrogen gas ll the tube cools down.
This is done to prevent hot copper from again
combining with oxygen to form copper(II)
oxide upon the entry of air.
Observa on: Black copper(II) oxide is reduced to reddish-brown copper metal.
CuO + H 2 Cu + H O
2
(black) (reddish-brown)
Conclusion: This shows that hydrogen is a strong reducing agent that reduced copper(II) oxide to copper.
USES OF HYDROGEN
• Hydrogen is used extensively in the produc on of ammonia (NH ) by
3
Haber’s process. Ammonia is widely used to manufacture fer lisers and
nitric acid.
• Hydrogen gas is also used to manufacture hydrochloric acid and methanol.
• Hydrogen gas is used in the prepara on of solid vanaspa ghee from
liquid vegetable oils such as palm oil, groundnut oil and coconut oil. In
this process, liquid vegetable oils are treated with hydrogen under
pressure in the presence of fi nely divided nickel, pla num or palladium as Fig. 7.4: Vanaspati ghee
a catalyst. This process is thus called cataly c hydrogena on of oils.
• Hydrogen is used in the produc on of oxy-hydrogen fl ame which is a
high temperature fl ame used for cu ng and welding of metals. This
fl ame has a temperature of about 2800°C.
• Liquid hydrogen is used as a fuel in rockets and guided missiles. This
is because it has high heat of combus on. Coal gas and water gas are
some hydrogen-based fuels.
• Hydrogen is used as a reducing agent in metallurgy to extract pure
metals from their oxides.
Fig. 7.5: Oxy-hydrogen fl ame
146