Page 97 - Start Up Mathematics_6
P. 97
Measuring Angles
To find the exact measure by which one angle is greater than the other is only possible if we
measure an angle in terms of some numerical value having a standard unit. The standard unit of
measurement of an angle is called a degree.
If a circle is divided into 360 equal parts, then each part is called a degree and is denoted by 1°.
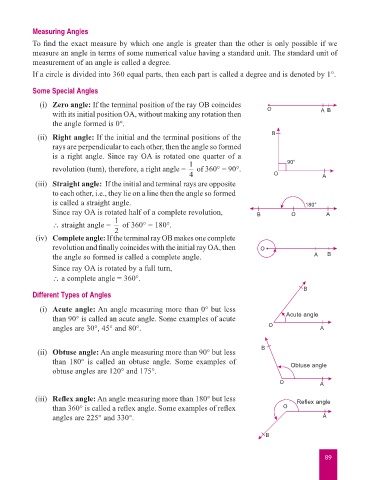
Some Special Angles
(i) Zero angle: If the terminal position of the ray OB coincides
with its initial position OA, without making any rotation then O A B
the angle formed is 0°.
(ii) Right angle: If the initial and the terminal positions of the B
rays are perpendicular to each other, then the angle so formed
is a right angle. Since ray OA is rotated one quarter of a
1 90°
revolution (turn), therefore, a right angle = of 360° = 90°.
4 O A
(iii) Straight angle: If the initial and terminal rays are opposite
to each other, i.e., they lie on a line then the angle so formed
is called a straight angle. 180°
Since ray OA is rotated half of a complete revolution, B O A
1
∴ straight angle = of 360° = 180°.
2
(iv) Complete angle: If the terminal ray OB makes one complete
revolution and finally coincides with the initial ray OA, then O
the angle so formed is called a complete angle. A B
Since ray OA is rotated by a full turn,
∴ a complete angle = 360°.
B
Different Types of Angles
(i) Acute angle: An angle measuring more than 0° but less
than 90° is called an acute angle. Some examples of acute Acute angle
angles are 30°, 45° and 80°. O A
(ii) Obtuse angle: An angle measuring more than 90° but less B
than 180° is called an obtuse angle. Some examples of Obtuse angle
obtuse angles are 120° and 175°.
O A
(iii) Reflex angle: An angle measuring more than 180° but less Reflex angle
than 360° is called a reflex angle. Some examples of reflex O
angles are 225° and 330°. A
B
89