Page 99 - Start Up Mathematics_6
P. 99
Example 10: Where will the hour hand of a clock stop if it starts
(a) from 5 and turns through 1 right angle?
(b) from 7 and turns through 3 right angles?
(c) from 2 and turns through 2 straight angles?
Solution: (a) 8 (b) 4 (c) 2
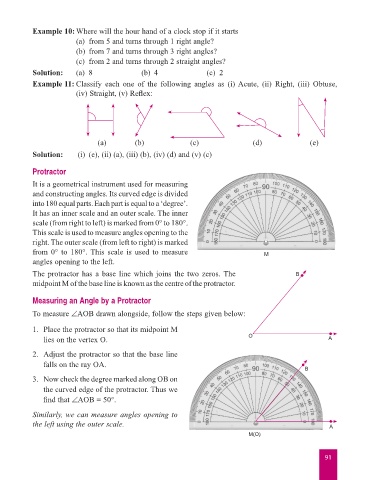
Example 11: Classify each one of the following angles as (i) Acute, (ii) Right, (iii) Obtuse,
(iv) Straight, (v) Reflex:
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Solution: (i) (e), (ii) (a), (iii) (b), (iv) (d) and (v) (c)
Protractor
It is a geometrical instrument used for measuring
and constructing angles. Its curved edge is divided
into 180 equal parts. Each part is equal to a ‘degree’.
It has an inner scale and an outer scale. The inner
scale (from right to left) is marked from 0° to 180°.
This scale is used to measure angles opening to the
right. The outer scale (from left to right) is marked
from 0° to 180°. This scale is used to measure M
angles opening to the left.
The protractor has a base line which joins the two zeros. The B
midpoint M of the base line is known as the centre of the protractor.
Measuring an Angle by a Protractor
To measure ∠AOB drawn alongside, follow the steps given below:
1. Place the protractor so that its midpoint M
lies on the vertex O. O A
2. Adjust the protractor so that the base line
falls on the ray OA.
B
3. Now check the degree marked along OB on
the curved edge of the protractor. Thus we
find that ∠AOB = 50°.
Similarly, we can measure angles opening to
the left using the outer scale. A
M(O)
91