Page 18 - ICSE Math 8
P. 18
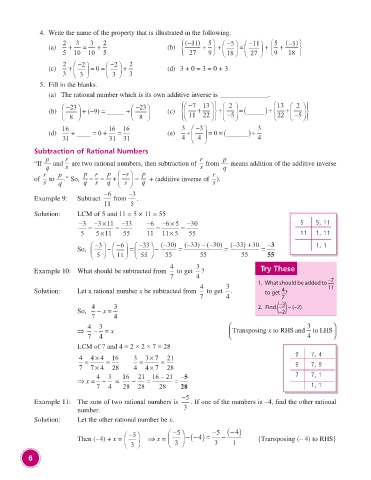
4. Write the name of the property that is illustrated in the following.
2 3 3 2 (−11 ) 5 5 −11 5 − ( 5 )
−
=
(a) + = + (b) + + + +
5 10 10 5 27 9 18 27 9 18
2 − 2 − 2 2
(c) + == + (d) 3 + 0 = 3 = 0 + 3
0
3 3 3 3
5. Fill in the blanks.
(a) The rational number which is its own additive inverse is ______________.
13
+
+
(b) −23 +−9( ) = _____ + −23 (c) −7 13 2 =(_____ )+ + 2
8 8 11 22 −5 22 −5
16 16 16 3 − 3 3
0 (______
(d) + ____ = 0 + = (e) + == ) +
31 31 31 4 4 4
Subtraction of Rational Numbers
p r r p
“If q and are two rational numbers, then subtraction of from q means addition of the additive inverse
s
s
r p p r p r − p r
of to q .” So, q − s = q + s = q + (additive inverse of ).
s
s
− −6 3
Example 9: Subtract from .
11 5
Solution: LCM of 5 and 11 = 5 × 11 = 55
−3 −×311 −33 −6 −×65 −30 5 5, 11
= = = =
×
5 511 55 11 11 × 5 55 11 1, 11
3 − −33 ( −30) ( −33) − −30( ) ( −333) + 30 −3 1, 1
− 6
=
−
So, − = = =
5 11 55 55 55 55 55
4 3 Try These
Example 10: What should be subtracted from to get ?
7 4 –7
4 3 1. What should be added to
11
4
Solution: Let a rational number x be subtracted from to get . to get ?
7 4 7
4 3 2. Find –3 – (–2).
So, −= –2
x
7 4
4 3 3
⇒ − = x Transposingto RHSandx to LHS
7 4 4
LCM of 7 and 4 = 2 × 2 × 7 = 28
2 7, 4
4 44× 16 3 37× 21
= = = = 2 7, 2
7 74× 28 4 47× 28
4 3 16 21 16 − 21 −5 7 7, 1
⇒ x = − = − = =
7 4 28 28 28 28 1, 1
−5
Example 11: The sum of two rational numbers is . If one of the numbers is –4, find the other rational
number. 3
Solution: Let the other rational number be x.
−
5 5 −− ( 4 ) = −5 − − ( 4 )
−
Then (–4) + x = ⇒ x = {Transposing (– 4) to RHS}
3 3 3 1
6