Page 13 - ICSE Math 4
P. 13
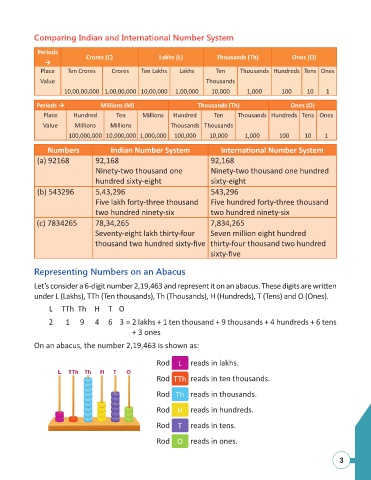
Comparing Indian and International Number System
Periods
Crores (C) Lakhs (L) Thousands (Th) Ones (O)
→
Place Ten Crores Crores Ten Lakhs Lakhs Ten Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones
Value Thousands
10,00,00,000 1,00,00,000 10,00,000 1,00,000 10,000 1,000 100 10 1
Periods → Millions (M) Thousands (Th) Ones (O)
Place Hundred Ten Millions Hundred Ten Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones
Value Millions Millions Thousands Thousands
100,000,000 10,000,000 1,000,000 100,000 10,000 1,000 100 10 1
Numbers Indian Number System Interna onal Number System
(a) 92168 92,168 92,168
Ninety-two thousand one Ninety-two thousand one hundred
hundred sixty-eight sixty-eight
(b) 543296 5,43,296 543,296
Five lakh forty-three thousand Five hundred forty-three thousand
two hundred ninety-six two hundred ninety-six
(c) 7834265 78,34,265 7,834,265
Seventy-eight lakh thirty-four Seven million eight hundred
thousand two hundred sixty-fi ve thirty-four thousand two hundred
sixty-fi ve
Representing Numbers on an Abacus
Let’s consider a 6-digit number 2,19,463 and represent it on an abacus. These digits are wri en
under L (Lakhs), TTh (Ten thousands), Th (Thousands), H (Hundreds), T (Tens) and O (Ones).
L TTh Th H T O
2 1 9 4 6 3 = 2 lakhs + 1 ten thousand + 9 thousands + 4 hundreds + 6 tens
+ 3 ones
On an abacus, the number 2,19,463 is shown as:
Rod L reads in lakhs.
L TTh Th H T O
Rod TTh reads in ten thousands.
Rod Th reads in thousands.
Rod H reads in hundreds.
Rod T reads in tens.
Rod O reads in ones.
3