Page 88 - Viva ICSE Computer Studies 7 : E-book
P. 88
Types of Database
There are basically two types of a database: fl at fi le database and relational database
• Flat File Database: A fl at fi le database stores data fi les that mainly contain records of fi xed
number of fi elds and without any structured relationship. Microsoft Excel is an example
of a fl at fi le database.
• Relational Database: A relational database organises data into a series of records held in
linked tables. Microsoft Access and Oracle are examples of relational database.
Structure of Database
Let’s now get familiar with the terminologies of a database.
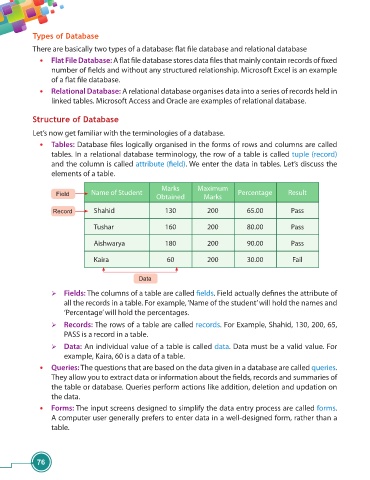
• Tables: Database fi les logically organised in the forms of rows and columns are called
tables. In a relational database terminology, the row of a table is called tuple (record)
and the column is called attribute (fi eld). We enter the data in tables. Let’s discuss the
elements of a table.
Marks Maximum
Field Name of Student Percentage Result
Obtained Marks
Record Shahid 130 200 65.00 Pass
Tushar 160 200 80.00 Pass
Aishwarya 180 200 90.00 Pass
Kaira 60 200 30.00 Fail
Data
Fields: The columns of a table are called fi elds. Field actually defi nes the attribute of
all the records in a table. For example, ‘Name of the student’ will hold the names and
‘Percentage’ will hold the percentages.
Records: The rows of a table are called records. For Example, Shahid, 130, 200, 65,
PASS is a record in a table.
Data: An individual value of a table is called data. Data must be a valid value. For
example, Kaira, 60 is a data of a table.
• Queries: The questions that are based on the data given in a database are called queries.
They allow you to extract data or information about the fi elds, records and summaries of
the table or database. Queries perform actions like addition, deletion and updation on
the data.
• Forms: The input screens designed to simplify the data entry process are called forms.
A computer user generally prefers to enter data in a well-designed form, rather than a
table.
76