Page 18 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 18
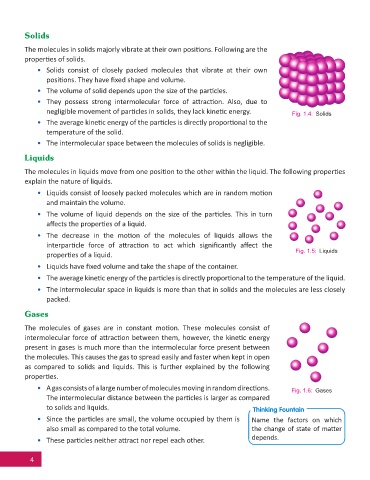
Solids
The molecules in solids majorly vibrate at their own posi ons. Following are the
proper es of solids.
• Solids consist of closely packed molecules that vibrate at their own
posi ons. They have fi xed shape and volume.
• The volume of solid depends upon the size of the par cles.
• They possess strong intermolecular force of a rac on. Also, due to
negligible movement of par cles in solids, they lack kine c energy. Fig. 1.4: Solids
• The average kine c energy of the par cles is directly propor onal to the
temperature of the solid.
• The intermolecular space between the molecules of solids is negligible.
Liquids
The molecules in liquids move from one posi on to the other within the liquid. The following proper es
explain the nature of liquids.
• Liquids consist of loosely packed molecules which are in random mo on
and maintain the volume.
• The volume of liquid depends on the size of the par cles. This in turn
aff ects the proper es of a liquid.
• The decrease in the mo on of the molecules of liquids allows the
interpar cle force of a rac on to act which signifi cantly aff ect the
Fig. 1.5: Liquids
proper es of a liquid.
• Liquids have fi xed volume and take the shape of the container.
• The average kine c energy of the par cles is directly propor onal to the temperature of the liquid.
• The intermolecular space in liquids is more than that in solids and the molecules are less closely
packed.
Gases
The molecules of gases are in constant mo on. These molecules consist of
intermolecular force of a rac on between them, however, the kine c energy
present in gases is much more than the intermolecular force present between
the molecules. This causes the gas to spread easily and faster when kept in open
as compared to solids and liquids. This is further explained by the following
proper es.
• A gas consists of a large number of molecules moving in random direc ons. Fig. 1.6: Gases
The intermolecular distance between the par cles is larger as compared
to solids and liquids.
Thinking Fountain
• Since the par cles are small, the volume occupied by them is Name the factors on which
also small as compared to the total volume. the change of state of ma er
depends.
• These par cles neither a ract nor repel each other.
4