Page 152 - ICSE Chemistry 8
P. 152
The displacement of hydrogen from water, dilute acids and alkalis, when they are treated with metals
placed above hydrogen, may be understood in terms of the ac vity series of metals.
Activity Series of Metals
Reac ve metals like sodium and calcium can easily replace hydrogen from acids or water whereas, metals
like copper, silver and mercury cannot replace hydrogen.
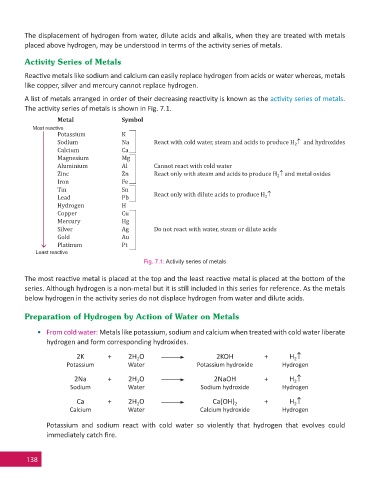
A list of metals arranged in order of their decreasing reac vity is known as the ac vity series of metals.
The ac vity series of metals is shown in Fig. 7.1.
Metal Symbol
Most reactive
Potassium K
Sodium Na React with cold water, steam and acids to produce H and hydroxides
2
Calcium Ca
Magnesium Mg
Aluminium Al Cannot react with cold water
Zinc Zn React only with steam and acids to produce H and metal oxides
2
Iron Fe
Tin Sn
Lead Pb React only with dilute acids to produce H
2
Hydrogen H
Copper Cu
Mercury Hg
Silver Ag Do not react with water, steam or dilute acids
Gold Au
Platinum Pt
Least reactive
Fig. 7.1: Activity series of metals
The most reac ve metal is placed at the top and the least reac ve metal is placed at the bo om of the
series. Although hydrogen is a non-metal but it is s ll included in this series for reference. As the metals
below hydrogen in the ac vity series do not displace hydrogen from water and dilute acids.
Preparation of Hydrogen by Action of Water on Metals
• From cold water: Metals like potassium, sodium and calcium when treated with cold water liberate
hydrogen and form corresponding hydroxides.
2K + 2H O 2KOH + H
2
2
Potassium Water Potassium hydroxide Hydrogen
2Na + 2H O 2NaOH + H
2
2
Sodium Water Sodium hydroxide Hydrogen
Ca + 2H O Ca(OH) 2 + H
2
2
Calcium Water Calcium hydroxide Hydrogen
Potassium and sodium react with cold water so violently that hydrogen that evolves could
immediately catch fi re.
138