Page 216 - ICSE Math 8
P. 216
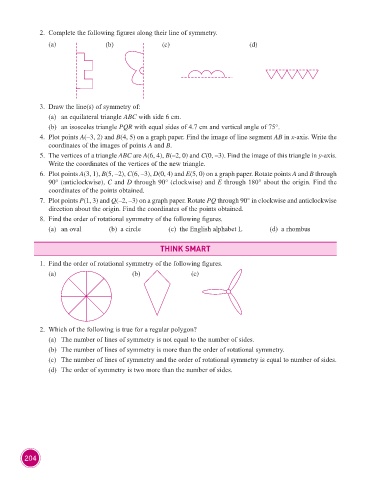
2. Complete the following figures along their line of symmetry.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
3. Draw the line(s) of symmetry of:
(a) an equilateral triangle ABC with side 6 cm.
(b) an isosceles triangle PQR with equal sides of 4.7 cm and vertical angle of 75°.
4. Plot points A(–3, 2) and B(4, 5) on a graph paper. Find the image of line segment AB in x-axis. Write the
coordinates of the images of points A and B.
5. The vertices of a triangle ABC are A(6, 4), B(–2, 0) and C(0, –3). Find the image of this triangle in y-axis.
Write the coordinates of the vertices of the new triangle.
6. Plot points A(3, 1), B(5, –2), C(6, –3), D(0, 4) and E(5, 0) on a graph paper. Rotate points A and B through
90° (anticlockwise), C and D through 90° (clockwise) and E through 180° about the origin. Find the
coordinates of the points obtained.
7. Plot points P(1, 3) and Q(–2, –3) on a graph paper. Rotate PQ through 90° in clockwise and anticlockwise
direction about the origin. Find the coordinates of the points obtained.
8. Find the order of rotational symmetry of the following figures.
(a) an oval (b) a circle (c) the English alphabet L (d) a rhombus
THINK SMART
1. Find the order of rotational symmetry of the following figures.
(a) (b) (c)
2. Which of the following is true for a regular polygon?
(a) The number of lines of symmetry is not equal to the number of sides.
(b) The number of lines of symmetry is more than the order of rotational symmetry.
(c) The number of lines of symmetry and the order of rotational symmetry is equal to number of sides.
(d) The order of symmetry is two more than the number of sides.
204