Page 260 - Start Up Mathematics_8 (Non CCE)
P. 260
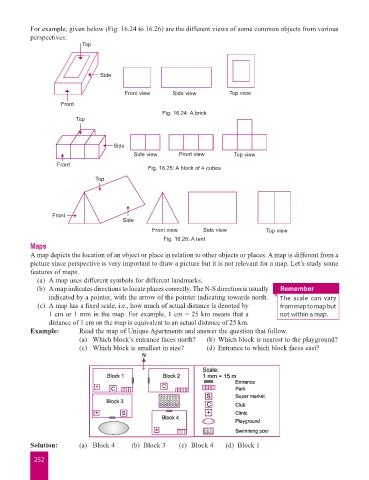
For example, given below (Fig. 16.24 to 16.26) are the different views of some common objects from various
perspectives:
Top
Side
Front view Side view Top view
Front
Fig. 16.24: A brick
Top
Side
Side view Front view Top view
Front
Fig. 16.25: A block of 4 cubes
Top
Front
Side
Front view Side view Top view
Fig. 16.26: A tent
Maps
A map depicts the location of an object or place in relation to other objects or places. A map is different from a
picture since perspective is very important to draw a picture but it is not relevant for a map. Let’s study some
features of maps.
(a) A map uses different symbols for different landmarks.
(b) A map indicates directions to locate places correctly. The N-S direction is usually Remember
indicated by a pointer, with the arrow of the pointer indicating towards north. The scale can vary
(c) A map has a fixed scale, i.e., how much of actual distance is denoted by from map to map but
1 cm or 1 mm in the map. For example, 1 cm = 25 km means that a not within a map.
distance of 1 cm on the map is equivalent to an actual distance of 25 km.
Example: Read the map of Unique Apartments and answer the question that follow.
(a) Which block’s entrance faces north? (b) Which block is nearest to the playground?
(c) Which block is smallest in size? (d) Entrance to which block faces east?
Solution: (a) Block 4 (b) Block 3 (c) Block 4 (d) Block 1
252