Page 186 - ICSE Math 6
P. 186
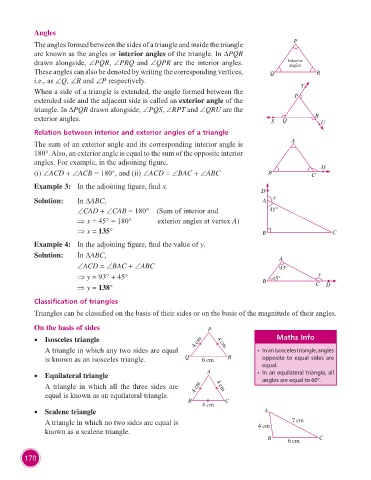
Angles
The angles formed between the sides of a triangle and inside the triangle P
are known as the angles or interior angles of the triangle. In DPQR
drawn alongside, ∠PQR, ∠PRQ and ∠QPR are the interior angles. Interior
angles
These angles can also be denoted by writing the corresponding vertices, Q R
i.e., as ∠Q, ∠R and ∠P respectively.
When a side of a triangle is extended, the angle formed between the T
extended side and the adjacent side is called an exterior angle of the P
triangle. In DPQR drawn alongside, ∠PQS, ∠RPT and ∠QRU are the
exterior angles. S Q R U
Relation between interior and exterior angles of a triangle
The sum of an exterior angle and its corresponding interior angle is A
180°. Also, an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior
angles. For example, in the adjoining figure, D
(i) ∠ACD + ∠ACB = 180°, and (ii) ∠ACD = ∠BAC + ∠ABC B C
Example 3: In the adjoining figure, find x.
D
Solution: In DABC, A x
∠CAD + ∠CAB = 180° (Sum of interior and 45°
⇒ x + 45° = 180° exterior angles at vertex A)
⇒ x = 135° B C
Example 4: In the adjoining figure, find the value of y.
Solution: In DABC, A
∠ACD = ∠BAC + ∠ABC 93°
⇒ y = 93° + 45° B 45° y
⇒ y = 138° C D
Classification of triangles
Triangles can be classified on the basis of their sides or on the basis of the magnitude of their angles.
On the basis of sides P
• Isosceles triangle 4 cm 4 cm Maths Info
A triangle in which any two sides are equal • In an isosceles triangle, angles
is known as an isosceles triangle. Q 6 cm R opposite to equal sides are
equal.
• Equilateral triangle A • In an equilateral triangle, all
angles are equal to 60°.
A triangle in which all the three sides are 4 cm 4 cm
equal is known as an equilateral triangle.
B C
4 cm
• Scalene triangle A
A triangle in which no two sides are equal is 4 cm 7 cm
known as a scalene triangle.
B 6 cm C
170