Page 81 - Viva ICSE Computer Studies 8 : E-book
P. 81
Selection Control Structure
A selection statement transfers a program control to a location depending on the result of the
conditional expression. If a condition evaluates to true, a set of statements present in a block
is executed, otherwise, a diff erent set of statements is executed. Java supports two types of
selection statements: if and switch.
If Control Structure
If control structure can be considered as bidirectional branching. When it executes a given
condition, the control is transferred to either of the two blocks of statements. There are three
types of If control structure.
• If statement
• If else statement
• If else if ladder
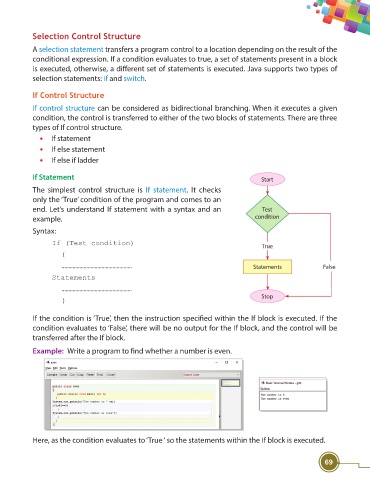
If Statement Start
The simplest control structure is If statement. It checks
only the ‘True’ condition of the program and comes to an
end. Let’s understand If statement with a syntax and an Test
example. condition
Syntax:
If (Test condition)
True
{
................................................... Statements False
Statements
...................................................
Stop
}
If the condition is ‘True’, then the instruction specifi ed within the If block is executed. If the
condition evaluates to ‘False’, there will be no output for the If block, and the control will be
transferred after the If block.
Example: Write a program to fi nd whether a number is even.
Here, as the condition evaluates to ‘True ‘ so the statements within the If block is executed.
69