Page 85 - Viva ICSE Computer Studies 8 : E-book
P. 85
Looping Control Structure
During programming, there comes certain situation when you need to repeat one or more
statements a number of times. This can be done by using loops. Looping is a process of
executing a block of statements again and again.
Let’s understand the concept of a loop with an example. You are taking part in a relay race of
1,600 metres. You are given a starting point. So you start from the given starting point and
keep running on the same track till the entire distance is not covered. This makes a loop of
running the same track again and again.
A loop must have a starting condition and also a terminating condition. The major advantage of
using loops is that they reduce the size of the program by reducing the number of instructions
and also save memory space. Java provides three types of looping control structures.
• For loop
• While loop
• Do while loop
A loop consists of the following parts.
• Control Variable: It defi nes the initial value which determines the duration of repetitions.
• Body of the Loop: It defi nes a set of statements which is executed within the loop
simultaneously.
• Test Condition: It defi nes whether the loop is to be repeated or it is to be terminated.
• Step Value: It defi nes the increment or decrement of the control variable.
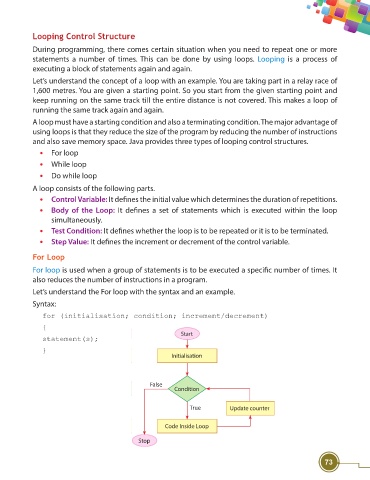
For Loop
For loop is used when a group of statements is to be executed a specifi c number of times. It
also reduces the number of instructions in a program.
Let’s understand the For loop with the syntax and an example.
Syntax:
for (initialisation; condition; increment/decrement)
{
Start
statement(s);
}
Initialisation
False
Condition
True Update counter
Code Inside Loop
Stop
73