Page 269 - Start Up Mathematics_7
P. 269
Drawing Solids on a Flat Surface
A paper is a flat surface. To draw solid shapes on it is difficult and needs some skills. In fact the
sketches are somewhat distorted to make them give an impression of 3-D objects. It’s a visual
illusion. The two commonly used techniques are explained below:
Oblique sketch
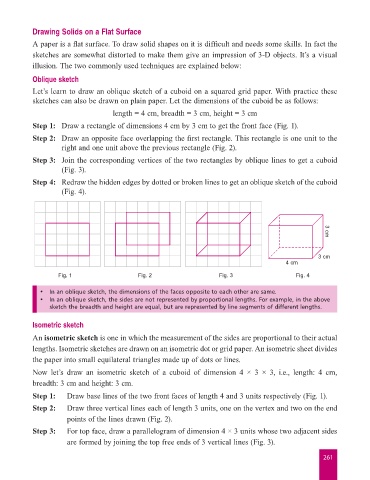
Let’s learn to draw an oblique sketch of a cuboid on a squared grid paper. With practice these
sketches can also be drawn on plain paper. Let the dimensions of the cuboid be as follows:
length = 4 cm, breadth = 3 cm, height = 3 cm
Step 1: Draw a rectangle of dimensions 4 cm by 3 cm to get the front face (Fig. 1).
Step 2: Draw an opposite face overlapping the first rectangle. This rectangle is one unit to the
right and one unit above the previous rectangle (Fig. 2).
Step 3: Join the corresponding vertices of the two rectangles by oblique lines to get a cuboid
(Fig. 3).
Step 4: Redraw the hidden edges by dotted or broken lines to get an oblique sketch of the cuboid
(Fig. 4).
3 cm
3 cm
4 cm
Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 3 Fig. 4
• In an oblique sketch, the dimensions of the faces opposite to each other are same.
• In an oblique sketch, the sides are not represented by proportional lengths. For example, in the above
sketch the breadth and height are equal, but are represented by line segments of different lengths.
Isometric sketch
An isometric sketch is one in which the measurement of the sides are proportional to their actual
lengths. Isometric sketches are drawn on an isometric dot or grid paper. An isometric sheet divides
the paper into small equilateral triangles made up of dots or lines.
Now let’s draw an isometric sketch of a cuboid of dimension 4 × 3 × 3, i.e., length: 4 cm,
breadth: 3 cm and height: 3 cm.
Step 1: Draw base lines of the two front faces of length 4 and 3 units respectively (Fig. 1).
Step 2: Draw three vertical lines each of length 3 units, one on the vertex and two on the end
points of the lines drawn (Fig. 2).
Step 3: For top face, draw a parallelogram of dimension 4 × 3 units whose two adjacent sides
are formed by joining the top free ends of 3 vertical lines (Fig. 3).
261