Page 84 - Start Up Mathematics_6
P. 84
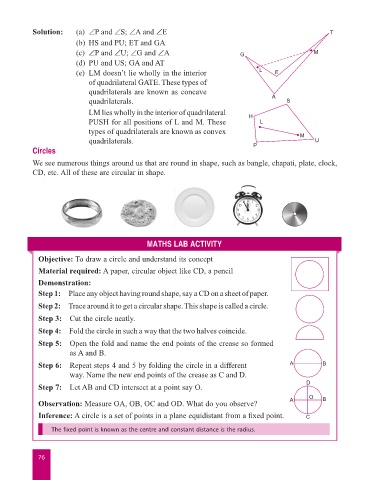
Solution: (a) ∠P and ∠S; ∠A and ∠E T
(b) HS and PU; ET and GA
(c) ∠P and ∠U; ∠G and ∠A G M
(d) PU and US; GA and AT
(e) LM doesn’t lie wholly in the interior L E
of quadri lateral GATE. These types of
quadrilaterals are known as concave
quadrilaterals. A S
LM lies wholly in the interior of quadrilateral H
PUSH for all positions of L and M. These L
types of quadrilaterals are known as convex M
quadrilaterals. U
Circles P
We see numerous things around us that are round in shape, such as bangle, chapati, plate, clock,
CD, etc. All of these are circular in shape.
MATHS LAB ACTIVITY
Objective: To draw a circle and understand its concept
Material required: A paper, circular object like CD, a pencil
Demonstration:
Step 1: Place any object having round shape, say a CD on a sheet of paper.
Step 2: Trace around it to get a circular shape. This shape is called a circle.
Step 3: Cut the circle neatly.
Step 4: Fold the circle in such a way that the two halves coincide.
Step 5: Open the fold and name the end points of the crease so formed
as A and B.
Step 6: Repeat steps 4 and 5 by folding the circle in a different A B
way. Name the new end points of the crease as C and D.
D
Step 7: Let AB and CD intersect at a point say O.
O B
Observation: Measure OA, OB, OC and OD. What do you observe? A
Inference: A circle is a set of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point. C
The fixed point is known as the centre and constant distance is the radius.
76