Page 143 - Start Up Mathematics_6
P. 143
1 3 7 8
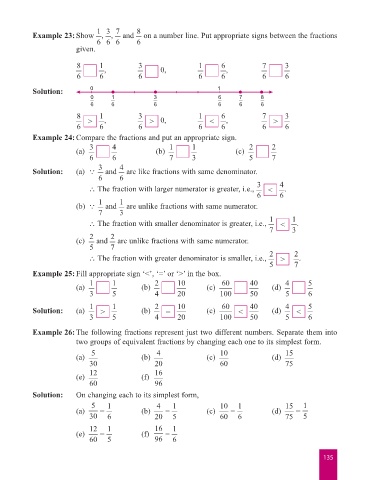
Example 23: Show , , and on a number line. Put appropriate signs between the fractions
6 6 6 6
given.
8 1 3 1 6 7 3
, 0, ,
6 6 6 6 6 6 6
Solution: 0 1
0 1 3 6 7 8
6 6 6 6 6 6
7
1
6
8 > , 3 > 0, 1 < , > 3
6 6 6 6 6 6 6
Example 24: Compare the fractions and put an appropriate sign.
3 4 1 1 2 2
(a) (b) (c)
6 6 7 3 5 7
3 4
Solution: (a) and are like fractions with same denominator.
6 6
4
3
∴ The fraction with larger numerator is greater, i.e., < .
6 6
1 1
(b) and are unlike fractions with same numerator.
7 3
1
1
∴ The fraction with smaller denominator is greater, i.e., < .
7
3
2
(c) 2 and are unlike fractions with same numerator.
5 7
2
2
∴ The fraction with greater denominator is smaller, i.e., > .
5 7
Example 25: Fill appropriate sign ‘<’, ‘=’ or ‘>’ in the box.
1 1 2 10 60 40 4 5
(a) (b) (c) (d)
3 5 4 20 100 50 5 6
1
Solution: (a) > 1 (b) 2 = 10 (c) 60 < 40 (d) 4 < 5
3 5 4 20 100 50 5 6
Example 26: The following fractions represent just two different numbers. Separate them into
two groups of equivalent fractions by changing each one to its simplest form.
(a) 5 (b) 4 (c) 10 (d) 15
30 20 60 75
12 16
(e) (f)
60 96
Solution: On changing each to its simplest form,
5 1 4 1 10 1 15 1
(a) = (b) = (c) = (d) =
30 6 20 5 60 6 75 5
12 1 16 1
(e) = (f) =
60 5 96 6
135