Page 9 - ICSE Math 8
P. 9
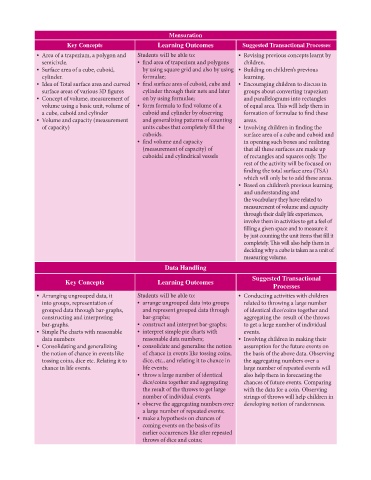
Mensuration
Key Concepts Learning Outcomes Suggested Transactional Processes
• Area of a trapezium, a polygon and Students will be able to: • Revising previous concepts learnt by
semicircle. • find area of trapezium and polygons children.
• Surface area of a cube, cuboid, by using square grid and also by using • Building on children’s previous
cylinder. formulae; learning.
• Idea of Total surface area and curved • find surface area of cuboid, cube and • Encouraging children to discuss in
surface areas of various 3D figures cylinder through their nets and later groups about converting trapezium
• Concept of volume, measurement of on by using formulae; and parallelograms into rectangles
volume using a basic unit, volume of • form formula to find volume of a of equal area. This will help them in
a cube, cuboid and cylinder cuboid and cylinder by observing formation of formulae to find these
• Volume and capacity (measurement and generalizing patterns of counting areas.
of capacity) units cubes that completely fill the • Involving children in finding the
cuboids. surface area of a cube and cuboid and
• find volume and capacity in opening such boxes and realizing
(measurement of capacity) of that all these surfaces are made up
cuboidal and cylindrical vessels of rectangles and squares only. The
rest of the activity will be focused on
finding the total surface area (TSA)
which will only be to add these areas.
• Based on children’s previous learning
and understanding and
the vocabulary they have related to
measurement of volume and capacity
through their daily life experiences,
involve them in activities to get a feel of
filling a given space and to measure it
by just counting the unit items that fill it
completely. This will also help them in
deciding why a cube is taken as a unit of
measuring volume.
Data Handling
Suggested Transactional
Key Concepts Learning Outcomes
Processes
• Arranging ungrouped data, it Students will be able to: • Conducting activities with children
into groups, representation of • arrange ungrouped data into groups related to throwing a large number
grouped data through bar-graphs, and represent grouped data through of identical dice/coins together and
constructing and interpreting bar-graphs; aggregating the result of the throws
bar-graphs. • construct and interpret bar-graphs; to get a large number of individual
• Simple Pie charts with reasonable • interpret simple pie charts with events.
data numbers reasonable data numbers; • Involving children in making their
• Consolidating and generalizing • consolidate and generalise the notion assumption for the future events on
the notion of chance in events like of chance in events like tossing coins, the basis of the above data. Observing
tossing coins, dice etc. Relating it to dice, etc., and relating it to chance in the aggregating numbers over a
chance in life events. life events; large number of repeated events will
• throw a large number of identical also help them in forecasting the
dice/coins together and aggregating chances of future events. Comparing
the result of the throws to get large with the data for a coin. Observing
number of individual events. strings of throws will help children in
• observe the aggregating numbers over developing notion of randomness.
a large number of repeated events;
• make a hypothesis on chances of
coming events on the basis of its
earlier occurrences like after repeated
throws of dice and coins;