Page 287 - ICSE Math 7
P. 287
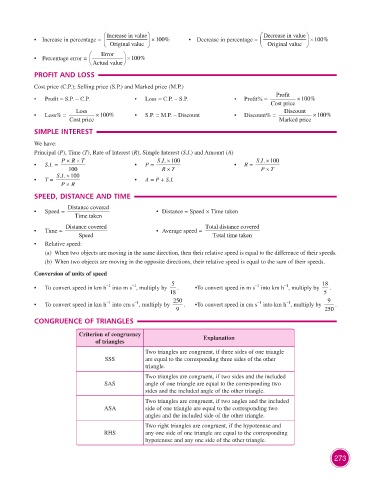
Increase in value Decrease in value
• Increase in percentage = × 100% • Decrease in percentage = × 100%
Original value Original value
Error
• Percentage error = × 100%
Actual value
PROFIT AND LOSS
Cost price (C.P.); Selling price (S.P.) and Marked price (M.P.)
Profit
• Profit = S.P. – C.P. • Loss = C.P. – S.P. • Profit% = × 100%
Cost price
Loss Discount
• Loss% = × 100% • S.P. = M.P. – Discount • Discount% = × 100%
Cost price Marked price
SIMPLE INTEREST
We have:
Principal (P), Time (T), Rate of Interest (R), Simple Interest (S.I.) and Amount (A)
P × RT× SI SI
. . 100×
. . 100×
• S.I. = • P = • R =
100 RT× PT×
. . 100×
SI
• T = • A = P + S.I.
P × R
SPEED, DISTANCE AND TIME
Distance covered
• Speed = • Distance = Speed × Time taken
Time taken
Distance covered Total distance covered
• Time = • Average speed =
Speed Total time taken
• Relative speed:
(a) When two objects are moving in the same direction, then their relative speed is equal to the difference of their speeds.
(b) When two objects are moving in the opposite directions, their relative speed is equal to the sum of their speeds.
Conversion of units of speed
–1
–1
–1
–1
• To convert speed in km h into m s , multiply by 5 . • To convert speed in m s into km h , multiply by 18 .
18 5
–1
–1
–1
–1
• To convert speed in km h into cm s , multiply by 250 . • To convert speed in cm s into km h , multiply by 9 .
9 250
CONGRUENCE OF TRIANGLES
Criterion of congruency Explanation
of triangles
Two triangles are congruent, if three sides of one triangle
SSS are equal to the corresponding three sides of the other
triangle.
Two triangles are congruent, if two sides and the included
SAS angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two
sides and the included angle of the other triangle.
Two triangles are congruent, if two angles and the included
ASA side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two
angles and the included side of the other triangle.
Two right triangles are congruent, if the hypotenuse and
RHS any one side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding
hypotenuse and any one side of the other triangle.
273